Common Valvular Heart Diseases Mitral stenosis (MS),Mitral regurgitation (MR),Aortic stenosis (AS) and Aortic regurgitation (AR)
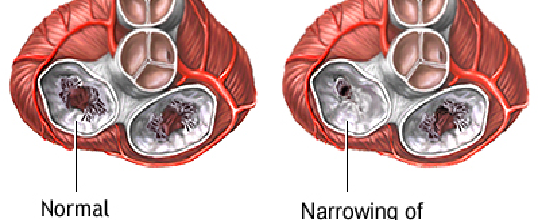
Mitral Stenosis (MS) Mitral Stenosis (MS) is a form of valvular heart disease characterized by the narrowing of the mitral valve orifice. The most common cause of mitral stenosis is rheumatic fever, though the stenosis typically does not become clinically relevant until several decades later. Mitral Regurgitation (MR) Mitral regurgitation (MR) also known as mitral […]