Furuncle Nostril
A furuncle in the nostril, also known as nasal vestibulitis or a nasal boil, is a painful, pus-filled infection of a hair follicle caused by bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus. Treatment varies by severity, but can include topical antibiotic ointments, warm compresses to help it drain, or oral antibiotics for more severe cases. In severe situations, a provider may need to drain the boil and administer intravenous (IV) antibiotics in rare cases.
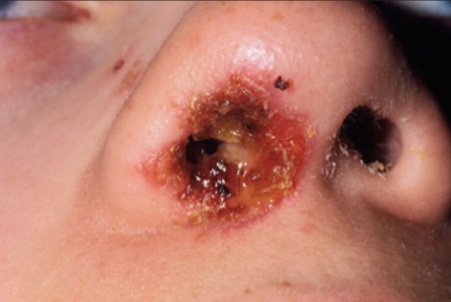
Causes of Furuncle Nostril
Bacterial infection, primarily from Staphylococcus aureus.
Minor cuts, irritation, or friction from hair plucking, nose picking, or excessive nose blowing.
Damaged skin from conditions like eczema or acne.
Using nasal steroid therapies.
Hyperemia of the affected area
Swelling
Pain at the site of the lesion
Pain when pressing
Increased body temperature (systemic symptom)
Symptoms of Furuncle Nostril
Pain, redness, and swelling inside the nostril.
A red or white, pimple-like bump or boil.
Crusting or yellow, crusty discharge.
Itching or soreness.
In the next stage (purulent furuncle), if measures are not taken in time or the treatment was inadequate, the symptoms become more complicated. The following is diagnosed:
Thrombus formation in the angular vein area (outwardly resembles a thickened cord)
Increase in general body temperature to significant values
Enlarged lymph nodes
Swelling of the eyelids, hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the eye, difficulty in moving the eyeballs, pain
Deterioration of vision
Bulging of the eye
In children
How to draw pus out of a boil? This question is often asked by parents. You should not look for traditional medicine recipes and treat the disease yourself. You do not need to buy medications in a pharmacy chain – on the advice of a familiar pharmacist. A boil in children can be a consequence of hidden pathologies, so you need to immediately consult a doctor.
In pregnant women
A boil in pregnant women threatens the health of both the woman and the fetus, so at an early stage of the disease you need to seek help. You cannot take antibiotics and other drugs on your own or squeeze out the formation. The purulent core of the boil is located quite deep, with illiterate attempts to pull it out, sepsis can develop.
Prevention of Furuncle Nostril
Preventive measures are not complicated and include: timely treatment of any chronic pathologies of the body, hardening procedures, exclusion of mechanical injuries, balanced nutrition, observance of personal hygiene rules and regular diagnostic procedures.
Treatment of Furuncle Nostril
Mild cases
Apply a topical antibiotic ointment, such as bacitracin or mupirocin, and use warm compresses to help it drain. Do not squeeze the boil.
Moderate to severe cases
A doctor may prescribe oral antibiotics.
Severe cases or those that don’t respond to antibiotics
A healthcare provider may need to surgically drain the boil and administer antibiotics through an IV.
For carriers
If you are found to be a carrier of the bacteria, the doctor may prescribe topical and/or oral antibiotics to help prevent recurrence and spread.
- Drainage
- Often antibiotics effective against MRSA
- Abscesses are incised and drained. Intermittent hot compresses are used to facilitate drainage.
- Antibiotics, when used, should be effective against MRSA, pending culture and sensitivity test results. In afebrile patients, treatment of a single lesion < 5 mm requires no antibiotics.
Systemic antibiotics are recommended for the following
Lesions > 5 mm or < 5 mm that do not resolve with drainage
Multiple lesions
Evidence of expanding cellulitis
Immunocompromise
Patients at risk of endocarditis
Fever
medlight2u.com
Acne Acne vulgaris Acute Renal Failure Adrenal cortex Angina Angina Pectoris Aortic Regurgitation (AR) Aortic Stenosis (AS) Chest pain Chronic pyelonephritis Coarctation of Aorta Cough cyanosis Cystic acne Dehydration depression Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosis of Aortic Stenosis Dr.KTS DR K TAMILSELVAN Fatigue Heart Failure Hypertension Hypokalemia Hypothyroidism Ischemic Heart Disease LBBB Mitral Incompetence Mitral insufficiency Mitral valve prolapse Nocturia Patent Ductus Arteriosus PDA Polyuria Proteinuria pulmonary hypertension Pulmonary Stenosis ST Depression Symptoms of Acne Syncope Treatment for acne valvular heart disease Ventricular Septal Defect VSD Zits