-

Sleeplessness (insomnia)
Sleeplessness, also called insomnia or sleep deprivation, means the state of being unable or unwilling to sleep adequately, leading to poor alertness, performance, and health, marked by difficulty falling or staying asleep, causing daytime…
-
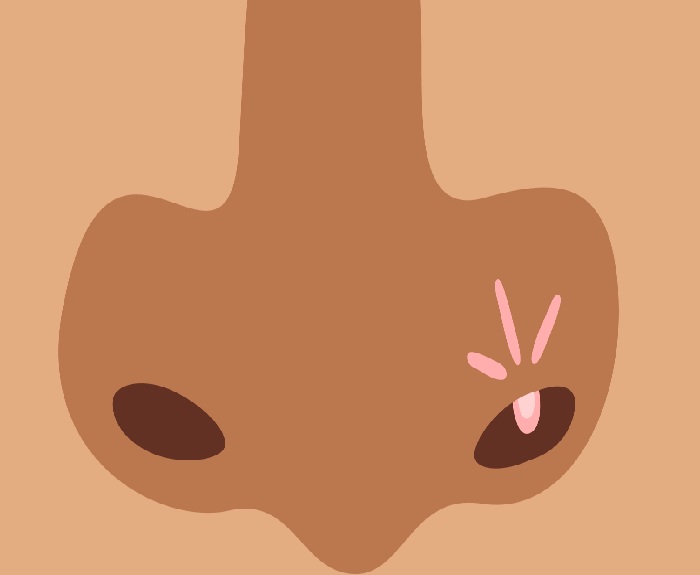
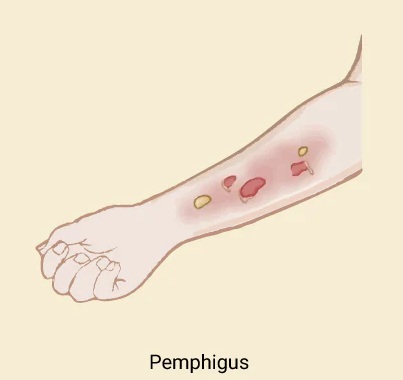
Furuncle Nostril
Furuncle Nostril A furuncle in the nostril, also known as nasal vestibulitis or a nasal boil, is a painful, pus-filled infection of a hair follicle caused by bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus. Treatment varies by…
-
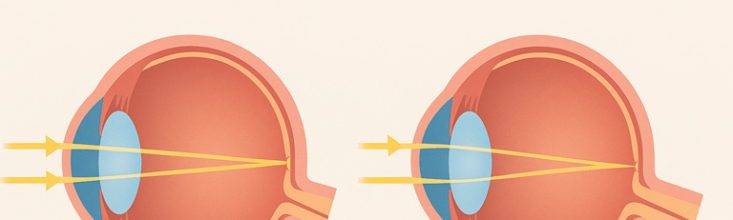
Presbyopia meaning “old eye”
Presbyopia meaning “old eye” Presbyopia comes from a Greek word meaning “old eye” and represents a natural part of ageing rather than a disease. This vision condition happens when your eye’s lens loses its…
-
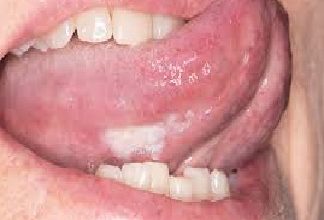
Oral cancer
Oral cancer Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer or cancer of the oral cavity, is a type of cancer that begins in the mouth, lips, or throat. The most common type is squamous…
-
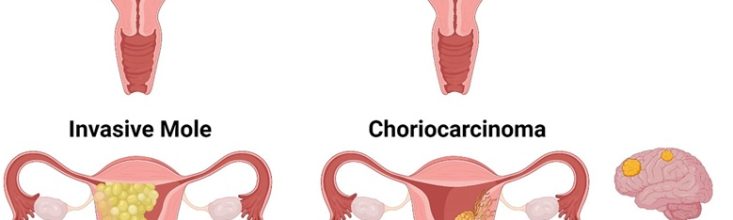
Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia (GTN)
Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia (GTN) is a type of gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) that is typically malignant. GTN arises from abnormal growth of placental tissue in the uterus and can include conditions like invasive…
medlight2u.com
A light on Practice of Medicine (The information provided is for informational and educational purposes only and should not be considered professional advice)
493
Posts written
320
Presentations
44M
Words Written

Dr KTS/Dr K TAMILSELVAN
When everything seems to be going against you, remember that the airplane takes off against the wind, not with it.
- "P" pulmonale
- "sixty-five roses" as a nickname
- 65 Roses
- Abdominal distention
- Abdominal pain
- abdomPeripheral embolic events
- About Diabetes Mellitus
- about PQRST in ECG
- About PQRST waves in ECG
- Acanthosis nigricans
- acetazolamide
- Acid and Corrosive Poisoning
- acid remains in the blood
- Acidemia
- Acidic urine.
- acidosis
- Acne
- Acne vulgaris
- ACS
- Action of CPR
- Active glomerulonephritis
- Active suicidal ideation
- Acute
- Acute caronary syndrome
- Acute Heart Failure
- Acute interstitial nephritis
- Acute kidney injury
- Acute leukemia
- Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)
- Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML)
- Acute Pancreatitis
- Acute Renal Failure
- Acute sinusitis
- Acute tubular necrosis
- Acute urethral syndrome
- Addison's disease
- Adenocarcinoma
- adenoidectomy
- Adenoids
- Adrenal cortex
- Adrenal glands
- adrenal medulla
- Advantages and disadvantages of CAPD
- Adynamic ileus
- Aetiology of Mitral Incompetence
- Aetiology of Pancreatitis
- AGXT
- alanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase
- Alcoholic pancreatitis
- alfa blocker
- Allergic Pnemonia
- Alopecia
- Alopecia areata
- alternative to haemodialysis
- aminoaciduria
- Aminoflycosides
- Amyloidosis
- Analgesic nephropathy
- Anaphylaxis
- Anatomical Classification of Pneumonia
- and hot lymph nodes
- Angina
- Angina Pectoris
- Angina Pectoris in ECG
- Angina symptoms
- anginal chest pain
- Anhidrotic asthenia
- Anorexia
- anti cancer drugs
- Antihistamines and anaphylaxis
- Antiplatelet drug therapy
- anxiety
- Anxiety Disorders
- Aortic Regurgitation
- Aortic Regurgitation (AR)
- Aortic root dilatation
- Aortic Stenosis (AS)
- ARF
- Armanni-Ebtein lesion
- arrhythmias
- arrhythmias in ECG
- Arteriolar injury
- arthrokatadysis
- Ascites
- Ascites with minimal oedema of feet
- ASD
- Associated defects of Coarctation of Aorta
- Associated defects of Complications of Aortic Stenosis
- Associated Diseases of Adrenal glands
- Atherosclerosis
- Atrial Enlargement Features in ECG
- Atrial Extrasystole
- Atrial Extrasystole Image
- Atrial septal defect
- Atrial Septal Defect in adults
- Atrial Septal Defect in children
- autoimmune blistering disease
- autoimmune disease
- Autosomal dominant Polycystic Kidney disease
- AV cushion defect
- Avascular Necrosis
- Bacterial endocarditis
- Bacterial sinusitis
- Bacteriuria
- Bad postures
- Bad prognosis in pneumonia
- balance disorders
- Balloon valvoplasty
- Balloon valvuloplasty
- Becker muscular dystrophy
- behavior
- Behavioral Instability
- Being very thirsty
- Benign glycosuria
- Bereavement
- betablockers
- Bicarbonate loss
- bicuspid aortic valve
- bifocals and progressive lenses
- Biopsy
- Biopsy to confirm brain tumors
- Bipolar Disorder
- Bird Flu
- Bird Flu Avian Influenza virus
- Bird Flu Avian Influenza virus of type A of subtype H5N1
- Biscuspid Aortic Valve
- Biventricular Failure
- Biventricular Hypertrophy
- black head
- bladder cancer
- bladder Malignancy
- Bladder outlet obstruction
- blister-like rash
- Blood clotting problems
- Blood glucose metabolism
- blood in the urine
- blood pH is low
- Blood sugar level is higher
- Blood urea to creatinine ratio
- Bluish color to the skin
- Blurry vision when reading up close
- BMI
- Body Imbalance
- Body Mass Index
- Bond with your baby.
- Bone marrow transplant.
- Boot shaped heart
- Borderline Personality Disorder
- Bowel decontamination
- Brain metastases
- Brain tumor Headaches
- Brain tumor symptoms by location
- Brain tumors
- Brain tumors in the lower part of the brain.
- Brain tumors in the middle of the brain.
- Breath sounds
- Breath that smells fruity
- breathing difficulty
- Breathing Patterns
- Broca's index
- Broken hairs
- Bronchial Breathing Sounds
- Bundle branch block
- Bundle branch block particularly LBBB
- burning pain on urination
- CAD
- calcitonin
- Calcium channel blockers
- cancer of the oral cavity
- CAPD
- Carcinoma of esophagus
- Cardiac catheterization
- Cardiac failure
- Cardiac infraction
- Cardiac massage
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) in infants
- Casts and Crystals
- Cat-scratch disease
- catabolic patients
- Catheterisation in Transposition of Great Vessels
- Causative agents of Anaphylaxis
- Causative organisms of UTI
- cause of cyanotic heart disease
- Causes and Risk Factors of Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia (GTN)
- Causes of bladder cancer
- Causes of abdominal distension
- Causes of Acanthosis nigricans
- Causes of Acute Renal Failure
- Causes of Alopecia
- Causes of Ascites
- Causes of Avascular Necrosis
- Causes of Body imbalance
- Causes of Brain tumors
- Causes of Cervical carcinoma
- Causes of congestive heart failure in the new born
- Causes of depression
- Causes of Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS)
- Causes of Fibromyalgia
- Causes of Furuncle Nostril
- Causes of Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome
- Causes of high output failure
- Causes of Hypokalemia
- Causes of Leukemia
- Causes of metabolic acidosis
- Causes of Mitral Regurgitation (MR)
- Causes of mood swings
- Causes of Muscular dystrophy
- Causes of Myositis
- Causes of Oral cancer
- Causes of Pemphigus
- Causes of Pneumonia
- Causes of Proximal Renal Tubular Acidosis
- Causes of psoriasis
- Causes of Pulmonary Oligaemia
- Causes of Rhabdomyolysis
- Causes of Shingles
- causes of sinus infections
- Causes of Sleeplessness
- Causes of Submandibular lymphadenitis
- Causes of suicidal ideation
- Causes of T Wave Inversion
- Causes of Truncus Arteriosus
- Causes of Unstable Angina
- Causes of Upper GI Bleeding
- Causes of Ventricular Hypertrophy
- CCF
- CCPD
- Cervical cancer
- Cervical carcinoma
- Cervical carcinoma or Cervical cancer
- cervix
- Characteristics of Transposition of Great Vessels
- Chemical Agents causing Pnemonia
- Chemoradiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Chemotherapy for Leukemia
- Chemotherapy of Pneumonia
- Chest Expansion
- Chest pain
- Chest x-ray and Barium swallow
- CHF
- Chickenpox
- Chorioadenoma Destruens
- Choriocarcinoma
- Choroid plexus tumors
- Chronic Complications of Diabetes
- Chronic glomerulonephritis
- Chronic Heart Failure
- chronic kidney disease
- Chronic leukemia
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
- Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)
- Chronic pyelonephritis
- chronic sinusitis
- Chronic urinary obstruction
- Cigarette smoking
- Cigarette Smoking and Cardiovascular Sequelae
- Cirrhotic ascites
- Classification of Ascites
- Classification of Diabetes
- Classification of Miliaria
- Clinical classification of Pnemonia
- Clinical classification of Pneumonia
- Clinical features of Acute Renal Failure
- Clinical features of Carcinoma of Esophagus
- Clinical Features of Diabetes
- Clinical features of heart failure
- Clinical features of Pancreatitis
- Clinical Features of Pneumonia
- Clinical Features of PRTA
- Clinical features of UTI
- Clinical presentation of Cystic Fibrosis
- Clinical presentation of Intestinal Tuberculosis
- Clinical types of Ischemic Heart Disease
- Clinical Variants of Pemphigus
- closed comedones
- Clubbing and cyanosis
- coagulopathy
- Coarctation of Aorta
- cognitive behavioral therapy
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia
- Cognitive difficulties
- Cognitive Instability
- Collagen vascular disease
- Colloid milium
- Color doppler of Mitral Incompetence
- Combination therapies for acne
- Common arterial trunk
- Common causes of Ascites
- Common Congenital Heart Diseases at Birth
- Common corrosive chemicals
- Common Heart Diseases at Birth
- Common Investigations of Urinary system
- Common Presbyopia Symptoms
- Common Symptoms and Investigations of Urinary system
- Common Symptoms of Urinary system
- Common triggers of Psoriasis
- Common Types of Pemphigus
- Common Valvular Heart Diseases Mitral stenosis (MS)
- Comparison of Type I and Type II Diabetes
- Complications Common to all valvular disease
- Complications following transplantation
- Complications of Psoriasis
- Complications of Acute Renal Failure
- Complications of Aortic Stenosis
- Complications of Ascites
- Complications of Coarctation of Aorta
- Complications of Cystic Fibrosis
- Complications of DNS
- Complications of Fibromyalgia
- Complications of Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome
- Complications of intestinal tuberculosis
- Complications of Miliaria
- Complications of Muscular dystrophy
- Complications of Myocardial Infarction
- Complications of pemphigus
- Complications of Pneumonia
- Complications of Shingles
- Complications of Tetrology of Fallot
- Complications of valvular heart disease
- Complications of Ventricular Hypertrophy
- Components of Tetrology of Fallot
- Composition of MYELIN
- Compression-only CPR
- Conclusion for Presbyopia meaning “old eye”
- Confusion or decreased alterness
- Congenital Aortic Stenosis
- Congenital Cardiac Defects
- Congenital muscular dystrophy
- congestive cardiac failure (CCF)
- congestive heart failure
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
- Consequences of Perinatal Mood and Anxiety Disorders (PMADs)
- Considerations of Unstable mind
- Contact with someone with chickenpox
- Contagious Alopecia
- Contagious of Alopecia
- Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis
- Continuous Cyclic Peritoneal Dialysis
- continuous dialysis
- Contraindications of Peritoneal Dialysis
- Convulsion
- Cooking fats
- Cooking oils
- Cor pulmonale
- corneal inlays eye surgery for presbyopia
- Corona virus
- Corona virus in detail
- Corona virus infection
- Coronary artery interventions
- Coronary Risk Factors
- Corrosive chemicals
- Couer en sabot
- Cough
- Cough syncope
- counselling
- COVID-19
- CPR in Pregnancy
- CPR involves
- Crackles
- Crohn’s disease
- Crohn’s disease or cancer
- Crusting of skin bumps
- CT scan (CAT scan)
- Cure for pimples
- Curved spine
- Curved spine (scoliosis)
- Cushing's syndrome
- cyanosis
- Cyanosis AT birth
- Cyanosis from birth
- Cyanotic Cardiac Defects
- Cyanotic Congenital Cardiac Defects
- cyanotic heart disease
- cyanotic heart disease after first year of life
- cyclothymic disorder
- Cystic acne
- Cystic Fibrosis
- Cystic Fibrosis (CF)
- Cystic Fibrosis (CF)"sixty-five roses" as a nickname
- Cystic Fibrosis Airway
- Cystinosis
- Cystitis and pyleonphritis
- cysts and abscesses
- Cysts in kidneys
- Cytomegalovirus
- Dacron patch
- damaged kidney
- DCMP
- deceased donor
- decreased plasma bicarbonates
- Decreased Potassium levels
- Decreased pulmonary blood flow
- Decreased urine output
- decreasedcability to think
- Defective tubular responsiveness
- Definition of Unstable Angina
- Dehydration
- Demyelinating diseases
- depressed mood
- depression
- Dermatomyositis
- Details about Diabetes Mellitus
- Development OF Myelin
- Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS)
- Dextro-Transposition of great arteries
- Diabetes Mellitus
- Diabetic glomerulosclerosis
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
- Diabetic nephropathy
- Diagnosis and Tests for headache
- Diagnosis for corona virus
- Diagnosis of Acanthosis nigricans
- Diagnosis of Acute caronary syndrome (ACS)
- Diagnosis of Adenoid disorders
- Diagnosis of Angina Pectoris
- Diagnosis of Aortic Stenosis
- Diagnosis of Ascites
- Diagnosis of Atrial Septal Defect
- Diagnosis of Avascular necrosis
- Diagnosis of Biscuspid Aortic Valve
- Diagnosis of Brain Tumors
- Diagnosis of Carcinoma of Esophagus
- Diagnosis of Cervical carcinoma
- Diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis
- Diagnosis of Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS)
- Diagnosis of Ebstein Anomaly
- Diagnosis of Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia (GTN)
- Diagnosis of Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome
- Diagnosis of headaches
- Diagnosis of Heart Failure
- Diagnosis of Hypokalemia
- Diagnosis of Intestinal Tuberculosis
- Diagnosis of Ischemic Heart Disease
- Diagnosis of Leukemia
- Diagnosis of Metabolic acidosis
- Diagnosis of Muscular dystrophy
- Diagnosis of Myocardial Infarction
- Diagnosis of Oral cancer
- Diagnosis of Pancreatitis
- Diagnosis of Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Diagnosis of PRTA
- Diagnosis of Renal Glycosurias
- Diagnosis of sinusitis
- Diagnosis of Stable Angina
- Diagnosis of suicidal ideation
- diagnosis of suicidal thoughts
- Diagnosis of Tetrology of Fallot
- Diagnosis of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
- Diagnosis of Transposition of Great Vessels
- Diagnosis of Unstable Angina
- Diagnosis of Upper GI Bleeding
- Diagnosis of UTI
- Diagnosis of Ventricular Septal Defect
- Diagnosis of VSD
- Diagnostic methods in Coarctation of Aorta
- dialysate
- dialyzer
- Diastolic Heart Failure
- Dieting
- Dieting with good aerobic exercise
- Dieting without good aerobic exercise
- Differential diagnosis of metabolic acidosis
- Differential diagnosis of Pancreatitis
- Differentiation between pleural rub and crackle
- Difficulty in Breathing
- Difficulty rising from a lying or sitting position
- Difficulty seeing in dim light
- Difficulty thinking
- Dilated aortic root
- Dilated cardiomyopathy
- Dilated pulmonary artery
- discolored patches of skin
- Disease of the heart valves
- diseased coronaries
- diseased kidney
- Diseases of Myelin
- Disequilibrium syndrome
- Disorders of Thyroid gland
- Dissection of ductus
- distractibility
- Dizziness
- DKA
- Dominant left ventricle
- Dominant right ventricle
- Down's syndrome
- DR K TAMILSELVAN
- DR TAMILSELVAN
- DR TAMILSELVAN K
- Dr.KTS
- DrKTS
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Dull note
- dyspnea
- Dyspnoea
- Early dialysis
- Ebstein Anomaly
- Ebstein's anomaly
- ECG
- ECG Features of Angina Pectoris
- ECG findings in Coarctation of Aorta
- ECG findings in Ebstein anamoly
- ECG findings in Tetrology of Fallot
- ECG findings in Ventricular Septal Defect
- ECG findings in VSD
- ECG findings of persistant truncus Arteriosus
- ECG of Mitral Incompetence
- Echo findings in Coarctation of Aorta
- Echo findings in Ebstein Anamoly
- Echo findings in Tetrology of Fallot
- Echo findings in VSD
- Effective cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- Egg shaped heart
- Eisenmenger syndrome
- Electro Convulsive Therapy (ECT)
- Electrocardiogram
- Electrocardiogram (ECG)
- Electrocoagulation
- electrolyte imbalances
- Elevated muscle enzyme levels
- Elevation of Blood Urea and Creatinine
- Embryonal tumors
- Emotional
- Emotional Instability
- End Stage Renal Disease
- End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
- Endocarditis
- Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
- Endoscopy
- Enlarged adenoids
- Enlarged pancreas
- enlarged thyroid
- enlargement of a lymph node
- Enteric hyperoxaluria
- Epithelioid Trophoblastic Tumor (ETT)
- Epstein-Barr virus
- Esophageal cancer
- Esophagoscopy
- ESRD
- Etienne-Louis Arthur Fallot
- Etiological Classification
- Etiology of Aortic Stenosis
- euphoria
- EVOLVING CHANGES
- Examinations for Pulmonary Stenosis
- Examples of Unstable mind
- excess of adipose tissue
- Excess of androgen secretion
- Excessive thirst
- Exertional syncope
- Extrapulmonary tuberculosis
- Extreme acidemia
- Extreme fatigue
- Eye Lens Changes with Age
- Eye strain and headaches
- Eye surgery for presbyopia
- facial pain
- Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy
- Factors governing cardiac function
- facts about myelin
- Failure of Bicarbonate Regeneration
- fainting spells
- Familial renal glycosuria
- Family relationships
- Fanconi syndrome
- Fatigue
- Features of Cystic Fibrosis
- Features of oral mucosal pemphigus
- Feeling guilty
- Feeling trapped
- Female diffuse hair loss-
- femoral head protrudes
- Fibromyalgia
- Findings in Acute Renal Failure
- Flattened T waves in ECG
- Food Values
- Forms of suicidal ideation
- Foul smelling sputum
- four anatomical abnormalities of the heart
- frank impetigo
- Frequent falls
- Functions of Adenoid
- Functions of Myelin
- Fungal sinusitis
- Furuncle Nostril
- gastrointestinal tuberculosis
- Germ cell tumors
- Gestational diabetes
- Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia (GTN)
- GFR
- Gliomas and related brain tumors
- Glomerular endothelial cell injury
- Glomerular filtration rate
- Glomerular haematuria
- Glomeruonephritis
- Glucocorticoids
- glucose is excreted in the urine
- Glycogen deposition in tubules
- glycosuria
- glycosylated hemoglobin
- goiter
- good aerobic exercise
- Grade I Obesity
- Grade II Obesity
- Grade III Obesity
- GRHPR
- Grief
- Gross electrolyte disturbance
- group of genetic diseases
- Guttate psoriasis
- H2 receptor antagonists
- H5N1 viruses
- Haematuria
- haemodialysis
- Haemodialysis and Peritoneal dialysis
- Haemoglobinuria
- Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome
- Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS)
- Haemorrhagic pancreatitis
- hair follicles
- Hair loss
- Happy Homoeopathy Clinic Erode
- Harmones of pituitary
- Hartnup disease
- HbA1c
- head of femur
- Headaches
- heart attack
- Heart Block
- Heart defect at birth
- Heart Diseases at Birth
- Heart Failure
- Heart Failure in a View
- Hemangioma
- hemolytic anaemia
- Hemolytic anemia
- Hemoptysis
- Hi2U Clinic
- High blood pressure
- High ketone levels in urine
- High Output Failure
- highly contagious viral infection
- Highly Pathogenic Avian Influenza virus
- Highly Suggestive Symptoms of Heart Disease
- History in Coarctation of Aorta
- History of "65 Roses"
- History of Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Holding reading material farther away
- Holt-Oram syndrome
- How corona virus spreads
- how healthy a food
- How to get away from Obesity
- How to support some one with bipolar disorder
- HPAI A
- HPV and Pap Test Results
- Human Leucocyte Associated Antigen
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
- HUS
- hydroxypyruvate reductase
- Hyper androgenism
- Hyper-resonant note
- Hyperacute Rejection
- Hyperaldosteronism
- Hyperchloremic
- hyperglycemia
- Hyperlipidemia
- Hypernephroma
- Hyperoxaluria
- Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis
- Hypertension
- Hypertensive nephrosclerosis
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
- Hypokalaemia
- Hypokalemia
- Hypokalemia in ECG
- hypomania
- Hypoplastic left heart syndrome
- hypopotassemia
- Hypothyroidism
- Hysterectomy
- I U V Picture
- I U V Picture in Renal Diseases
- I'm going to kill myself
- Ideal body weight
- Ideal gross body weight
- Idiopathic hyperoxaluria
- IHD
- ilioischial line
- Image of the Pituitary gland
- Imaging of Urinary System
- Immunosuppression
- Immunotherapy
- Important sources of cholesterol
- Important sources of iron
- Important sources of Proteins
- Incidence of congenital heart disease
- Increased Anion Gap
- Increased pulmonary blood flow
- Increased serum glycolic acid
- Increased urination
- Indications for Dialysis
- Infant health
- infarction
- inflammation in muscles
- inflammation of the lungs
- inflammation of the tissues in your sinuses
- inflammatory arthritis
- Inflammatory conditions of myositis
- Inflammatory lesion of acne
- influenza A or B
- Influenza and para influenza
- Infundibular pulmonary stenosis
- Inherited fructose intolerance
- Initial lesion of acne
- Inner ear issues
- Inner ear surgery
- insomnia
- Insulin dependent diabetes and kidney transplantation
- interesting facts about adenoids
- Intermittent peritoneal dialysis
- Intestinal Features of Cystic Fibrosis
- INTESTINAL TB
- Intestinal Tuberculosis
- Intra renal causes
- Intravenous Urography (IVU)
- Introduction about corona virus
- Invasive Mole
- Inverted AVR in ECG
- Investigations for corona virus
- Investigations of Acute Renal Failure
- Investigations of hypokalemia
- Investigations of Pneumonia
- Investigations of Upper GI Bleeding
- Investigations of Urinary system
- IPD
- Irregular abnormal Breathing Patterns
- irreversible renal failure
- Irrittable
- Ischemic cardiomyopathy
- Ischemic Heart Disease
- Isotope Renal Scans
- itchy
- jugular catheter
- JVP- prominent 'a' waves
- Kayser-Fleischer rings
- keratinazation
- Ketones in urine
- Key Points about Avascular Necrosis
- kidney Cysts
- Kidney failure
- Kidney Transplantation
- kidneys can no longer filter waste from the blood
- kinds of muscular dystrophy
- Klebsiella
- Klebsiella Pneumonia
- Kussmaul's breathing
- Laboratory findings in Tetrology of Fallot
- Labyrinthectomy
- Laparoscopy
- Large pulmonary arteries
- Largest endocrine gland
- Laser photocoagulation
- Laser therapy
- Lasik eye surgery for presbyopia
- LBBB
- leaking of blood from the left ventricle
- Left Atrial Enlargement
- Left Atrial Enlargement CXR
- left axis deviation
- Left bundle branch block
- Left sided Failure
- Left sided heart Failure
- Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
- Legionella pneumonia
- lens function
- Leptospirosis
- Less platelets
- less sleep
- Less Suggestive Symptoms of Heart Disease
- Leucocytosis
- Leukemia and Flow Cytometry
- Leukemia-Commonly as Blood Cancer
- Leukemia/Lymphoma Phenotyping Evaluation by Flow Cytometry
- Life expectancy in End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
- Life stages of Mood swings
- life-threatening complication of diabetes
- lifestyle.
- Limb-girdle muscular dystrophy
- living donor
- Lobar Pneumonia
- Lobular Pneumonia
- Location of Adenoid
- loss of interest
- Loss of lens elasticity after 40
- lung infection
- lung parenchyma
- LVH
- Lymphocytic leukemia
- Male pattern hair loss
- Malignancy of Urinary Bladder
- Malignancy of Urinary Tract
- Malignancy of Urinary Tract-Bladder
- man-made membrane
- Management in Aortic Stenosis
- management in End Stage Renal Disease
- Management of Psoriasis
- Management of Acanthosis nigricans
- Management of Anaphylaxis
- Management of Heart failure
- Management of Hypokalemia
- Management of Myocardial Infarction
- Management of obesity
- mania
- manic depression
- Marfan syndrome
- Marfan's syndrome
- Maternal health
- Measures to stop mood swings
- Mechanisms of VSD closure
- Medical Management for Deviated Nasal Septum
- Medical management for Mitral stenosis
- Medications for headaches
- Medullary sponge kidney
- Medullary sponge kidneys
- melanin deposits
- memory loss
- Meningiomas
- mental disorder
- mental health
- Mental health conditions related with Mood swings
- MERS
- metabolic acidosis
- Metastatic brain tumors
- Methods of Calculation of GFR
- Microvascular angina
- migraine
- Miliaria
- Miliaria profunda
- Miliaria pustulosa
- Miliaria Rubra
- Miliarial hypo hidrosis
- Mitral annulus calcification
- Mitral arcade
- Mitral diastolic flow murmur
- Mitral Incompetence
- Mitral Incompetence/Mitral regurgitation (MR) or mitral insufficiency
- Mitral insufficiency
- Mitral regurgitation
- Mitral regurgitation (MR)
- Mitral Stenosis (MS)
- Mitral valve
- Mitral valve prolapse
- mood swings
- Mood swings of adolescence
- Mood swings of menopause
- Mood swings of postpartum
- Mood swings of pregnancy
- Morning sneezing
- Mostly autosomal recessive
- Mouth cancer staging
- mouth-to-mouth respiration
- MR
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
- Multifocal and monovision contact lenses
- Muscle cramps
- Muscle invasive tumours in bladder
- Muscle pain
- Muscle pain and tenderness
- muscle tissue breaks down
- muscle tissue breaks down and releases its contents into the bloodstream
- muscle weakness
- Muscular dystrophy
- Muscular dystrophy (MD)
- Mustard procedure
- MVP
- Mycobacterium bovis
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis
- Mycoplasma pneumonia
- Myelin
- Myelin degeneration
- Myelogenous leukemia
- Myocardial hibernation
- Myocardial Infarction
- Myotonic muscular dystrophy
- Narrow pulse pressure
- Nasal endoscopy
- neonate's ductus arteriosus
- Nephro calcinosis
- nephrolithiasis
- nephrons
- Nephrosclerosis
- nephrotoxic medications
- Nerve damage
- Nerve tumors
- Neurodegeneration
- Neurogenic bladder
- neurotransmiters
- nifedipine
- No machine involved dialysis
- Nocturia
- Non-Atherosclerotic Causes
- Noncoronary interventions
- Nondiabetic glycosuria
- Nonglomerular haematuria
- Noonan's syndrome
- norepinephrine
- Normal Anion Gap
- Normal BMI
- Normal Potassium Levels
- Normal to decreased pulmonary blood flow
- Normoglycemic Hypercalciuria
- NSTEMI
- Nutritional values
- Obese people
- Obesity
- Obesity in detail
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Obstruction to renal arteries and veins
- Obstructive uropathy
- Occlusion miliaria
- Oliguria
- ophthalmology
- Oral cancer
- oral cavity cancer
- Orthopnoea
- osteogenesis imperfecta
- osteomalacia
- Other brain tumors
- Other causes of Myelin Degeneration
- Other conditions that can cause glycosuria
- Other treatments for Body balance
- Otto pelvis
- Over weight
- Oxalate poisioning
- oxalosis progressive
- P axis to left
- P duration and amplitude both increased
- P wave in ECG
- Paget’s disease
- pain after a viral illness
- painful rash caused by the Varicella-Zoster Virus
- Palpillary muscle dysfunction
- Palpitation
- pancreas
- Pancreatitis
- panzootic
- papillary necrosis
- Papules
- Paraganglioma
- Passive suicidal ideation
- Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Pathogenesis of diabetes
- PDA
- Pemphigus
- Pemphigus Foliaceus
- Pemphigus vulgaris
- Percussion Note
- Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)
- percutaneous interventional closure
- Perinatal mood and anxiety disorders (PMADs)
- Peritoneal Dialysis
- Peritoneal Dialysis catheter
- peritoneum
- Persistant Truncus Arteriosus
- Persistent Headache
- person’s mood
- PET scan (Positron Emission Tomography scan)
- pH of urine
- Pheripheral edema
- Physical agents causing Pnemonia
- Physical Examination findings in Coarctation of Aorta
- Physical Examination findings in Ebstein anamoly
- Physical Examination findings of aortic stenosis
- Physical Examination for Truncus Arteriosus
- Physical Examination of Mitral Incompetence
- Physical Examination of Tetrology of Fallot
- Physiology of Thyroid gland
- pilo-sebaseous duct
- Pilocarpine eye drops
- Pimples
- Pimples management
- Pineal tumors
- pituitary
- Pituitary and its Hormones with their Regulatory Hypothalamic Factors
- Pituitary gland
- Pituitary Gland and its Hormones
- Pituitary Gland and its Hormones with Hypothalamic Factors
- Pituitary Gland and its Hormones with their Regulatory Hypothalamic Factors
- Pituitary gland picture
- Pituitary tumors
- PKD
- PKD in medicine
- Placental-Site Trophoblastic Tumor (PSTT)
- plaques of skin
- plasma exchange
- Platypnoea
- Pleural Rub
- Pneumococcal
- Polycystic disease
- Polycystic Kidney Disease
- polydipsia
- Polymyositis
- Polyuria
- Poor nutrition
- Poor wound healing after kidney transplantation
- Porphyria
- Possible indications for short term dialysis
- Post miliarial hypo hidrosis
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Postherpetic neuralgia
- Postpartum Depression (PPD)
- Postpartum psychosis
- potassium depletion
- PQRST in ECG
- Prazosin
- Pre transplantation Recipient Preparation
- Pre-renal causes of ARF
- Precautions of Anaphylaxis
- Predisposing Factors of Pneumonia
- Predominant pustules
- Premature P wave in ECG
- presbyopia and farsightedness
- Presbyopia meaning “old eye”
- Presbyopia Treatment
- Prevention for Cervical carcinoma
- Prevention of Chicken Pox
- Prevention of End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
- Prevention of headaches
- Prevention of Oral cancer
- Preventions of Anaphylaxis
- Prickly heat
- Primary and Secondary headaches
- Primary brain tumors
- primary complication of PD
- primary headache
- Primary hyperoxaluria
- primary protrusio acetabuli
- Primary tubular transport defects
- Principles in Ischemic Heart Disease
- Prinzmental Angina
- Prinzmetal Angina
- Procedure of Flow cytometry
- Prognosis after kidney transplantation
- Prognosis in Leukemia
- Prognosis of Acute Renal Failure
- Prognosis of Alopecia
- Prognosis of Carcinoma of Esophagus
- Prognosis of Cervical carcinoma
- Prognosis of Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia (GTN)
- Prognosis of Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome
- Prognosis of Headaches
- Prognosis of Mitral Incompetence
- Prognosis of Myocardial Infarction
- Prognosis of Pancreatitis
- Prognosis of PRTA
- Prognosis of Pulmonary Stenosis
- Prognosis of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
- Prognosis of Unstable Angina
- Prognosis old Bladder cancer
- Progression of Muscular dystrophy
- prolongation of the PR interval in ECG
- Prominent U waves in ECG
- Prone position Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
- prostacyclin
- Prostatic hypertrophy
- Proteinuria
- Protrusio Acetabulum
- Proximal Renal Tubular Acidosis
- Proximal Renal Tubular Acidosis (Type II)
- Proximal RTA Type II
- proximal tubular glucose reabsorption
- proximal tubule
- PS
- Psoriasis
- Psoriasis unguis
- Psychological treatments
- Psychology
- psychotherapy
- Pulmanory plethora
- pulmonary arterial lumen
- Pulmonary atresia
- Pulmonary ejection click
- Pulmonary embolism
- Pulmonary features of Cystic Fibrosis
- pulmonary hypertension
- Pulmonary oligemia
- Pulmonary plethora
- Pulmonary Stenosis
- pulmonary valve
- Pulseless Electrical Activity (PEA)
- Pulsus parvus
- pustule bursts
- pyelonephritis
- Q wave in ECG
- QRS complex in ECG
- R and T waves in ECG
- R-R interval in ECG
- racing thoughts
- Radiation therapy
- Radiation therapy.
- Radiographic nephrocalcinosis
- Rales
- rare anatomic pattern of the hip
- Rastelli Procedure
- Raynaud's
- Raynaud's phenomenon
- Recurrence of glomerulonephritis
- Recurrent Headache
- Recurrent kidney infection
- Recurrent pneumonia
- Recurrent sinusitis
- Recurrent sneezing
- red and bumpy rash
- Redness around the skin eruptions
- Reduced accommodation ability of the eye
- Refractory Heart Failure
- Regional variations of Psoriasis
- Regular abnormal Breathing Patterns
- Regulation of Thyroid harmones
- Relaxation techniques
- Renal artery stenosis
- Renal carbuncle
- renal carcinoma
- Renal diabetes
- Renal Disease with Jaundice
- Renal Disease with large kidneys
- Renal Failure with Hemoptysis
- Renal Glycosurias
- Renal impairment
- Renal Pathology in Diabetes
- Renal tuberculosis
- Renal tubular acidosis
- Renal Tubular Dysfunction
- Renal ultrasonnography
- Renovascular hypertension
- Renovascular insufficiency
- respiratory acidosis
- Result of corona virus
- Rhabdomyolysis
- rheumatoid arthritis
- Rhinoplasty
- Rhonchi
- Richard Weiss
- Right Atrial Enlargement
- Right sided Failure
- right ventricular hypertrophy
- Right Ventricular lift
- Risk factors for avascular necrosis
- Risk Factors for Depression
- Risk factors for esophageal cancer
- Risk factors in Leukemia
- Risk factors of Angina Pectoris
- Risk factors of Cervical carcinoma
- Risk factors of Fibromyalgia
- Risk Factors of Mood swings
- Risk Factors of Perinatal mood and anxiety disorders (PMADs)
- Risk factors of Pneumonia
- Risk factors of Shingles
- Risk Factors of Submandibular lymphadenitis
- Risk factors of Unstable Angina
- Risk of Diabetes
- Role of the ciliary muscle in Presbyopia
- Romihilt Scoring system
- runny nose
- Rupture of ductus
- Rupture or dissection of ductus
- S2 single and loud
- Sadness
- SARS
- scaly papules
- Scarring Alopecia
- Scarring of the skin
- scoliosis
- Screening for Cervical carcinoma
- Seborrheic dermatitis
- second heart sound single and loud
- Secondary headache
- secondary osteoarthritis
- Secondary tubular transport defects
- Seizures due to Brain tumors
- Self Test to find deviated nasal septum
- Septoplasty
- serotonin
- Serum amylase > 200
- shingles
- Shortness of breath
- Signs and Symptoms Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia (GTN)
- Signs and symptoms of Aortic Stenosis
- Signs and symptoms of Ascites
- Signs and symptoms of corona virus
- Signs and Symptoms of Heart Disease
- Signs and Symptoms of Heart Failure
- Signs and Symptoms of Ischemic Heart Disease
- Signs and Symptoms of metabolic acidosis
- Signs and symptoms of Miliaria
- Signs and symptoms of Myocardial Infarction
- Signs and Symptoms of Respiratory Diseases
- Signs and symptoms of Unstable Angina
- Signs of Heart Disease
- Signs of Heart Failure
- Signs of metabolic acidosis
- Signs of Pulmonary Stenosis
- Signs of Respiratory Diseases
- Signs of Sleeplessness
- Signs of suicidal ideation
- Signs of suicidal intent
- Signs of Ventricular Septal Defect
- Signs of VSD
- Similar to corona virus
- similar to hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS)
- Single gene defects
- Single gene defects and congential heart disease
- Single S2
- sinuses
- Sinusitis
- sixty-five roses
- Sjogren syndrome
- skin disorder
- skin to build up into bumpy
- skin with keratinazation
- Sleep study
- Sleeping too little
- Sleeplessness
- Sleeplessness (insomnia)
- small and itchy rashes
- sneezing
- Sneezing recurrent episodes
- solution for pimples
- Spanish flu
- Special features of Pneumonia
- Specific Gravity of Urine
- Spinal fixation
- Spinal fusion
- Spinal headaches
- Splenectomy
- Sputum
- Squamous cell carcinoma
- ST Depression
- ST depression and T inversion in ECG
- ST Depression in ECG
- ST Elevation
- ST Elevation in ECG
- ST segment in ECG
- Stable angina
- Stages of Esophageal Cancer
- Stages of of Cervical carcinoma
- Staphylococcal Pneumonia
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Statin therapy
- Stereotactic radiosurgery for acoustic neuroma
- Steven Johnson syndrome.
- Stigma
- Stricture urethra
- structure of poly kidney disease
- stuffy nose
- Sub aortic stenosis
- subacute
- Submandibular lymphadenitis
- Subvalvular Aortic stenosis
- Subvalvular pulmonary stenosis
- Succussion Splash
- Sudamina
- Sudden cardiac failure
- Sudden death
- suicidal ideation
- Suicidal ideation always prevalent
- Suicidal ideation is not uncommon
- Suicidal ideation scale
- Suicidal intent
- Suicidal thoughts
- Suicide
- Suicide prevention
- superficial bladder Malignancy
- Superficial tumours in bladder
- superimposed coronaries
- support someone with bipolar disorder
- Supra valvular Aortic Stenosis
- suprarenal glands
- Supravalvular pulmonary stenosis
- Surgery options in
- Surgery to reconstruct the mouth
- Surgery to remove lymph nodes in the neck
- Surgical Management for DNS
- Surgical Management for Mitral stenosis
- Surgical treatment for Mitral Incompetence
- Sweating
- swelling of the lymph nodes
- Swollen
- Symptoms and Causes of Headaches
- Symptoms and Investigations of Urinary system
- Symptoms and signs of Anaphylaxis
- Symptoms of Acanthosis nigricans
- Symptoms of Acid and Corrosive Poisoning
- Symptoms of Acid Poisoning
- Symptoms of Acne
- Symptoms of Alopecia
- Symptoms of Aortic Stenosis
- Symptoms of Aortic Stenosis (AS)
- Symptoms of Atrial Septal Defect
- Symptoms of avascular necrosis
- Symptoms of bipolar disorder
- Symptoms of bladder cancer
- Symptoms of body imbalance
- Symptoms of Brain Tumors
- Symptoms of Carcinoma of Esophagus
- Symptoms of Cervical carcinoma
- Symptoms of Chicken Pox
- Symptoms of Corrosive Poisoning
- Symptoms of Cystic Fibrosis
- Symptoms of demyelinating diseases
- Symptoms of depression
- Symptoms of Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS)
- Symptoms of Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)
- Symptoms of End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
- Symptoms of Fibromyalgia
- Symptoms of Furuncle Nostril
- Symptoms of Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome
- Symptoms of Heart Disease
- Symptoms of Heart Failure
- Symptoms of Intestinal Tuberculosis
- Symptoms of Leukemia
- Symptoms of metabolic acidosis
- Symptoms of Mitral Regurgitation (MR)
- Symptoms of Muscular dystrophy
- Symptoms of Oral cancer
- Symptoms of Perinatal Mood and Anxiety Disorders (PMADs)
- Symptoms of Pneumonia
- Symptoms of PRTA
- Symptoms of Psoriasis
- Symptoms of Pulmonary Stenosis
- Symptoms of Renal Glycosurias
- Symptoms of Respiratory Diseases
- Symptoms of Rhabdomyolysis
- Symptoms of Shingles
- Symptoms of sinusitis
- Symptoms of Submandibular lymphadenitis
- Symptoms of Suicidal ideation
- Symptoms of Truncus Arteriosus
- Symptoms of Urinary system
- Symptoms of Ventricular Hypertrophy
- Symptoms of Ventricular Septal Defect
- Symptoms of VSD
- Syncope
- syndrome of microangiopathic hemolytic anaemia
- T wave in ECG
- T Wave Inversion
- T3
- T4
- Ta Segment
- Talking excessively
- Tall pointed T waves in ECG
- Tall T Waves in ECG
- Tall T Waves in Precordial Leads
- Targeted therapy
- Technical complications after kidney transplantation
- tender
- Test for corona virus
- Tests of Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome
- Tests used for cervical cancer staging
- Tetraiodothyronine
- tetraiodothyronine (T4)
- Tetrology of Fallot
- TGV
- The grades of the tumor
- The main part of the brain is called the cerebrum
- The phases of Leukemia Treatment
- The survival rate of leukemia
- The Term Unstable mind
- The types of headaches
- Therapies for Sleeplessness
- Therapy for Avascular Necrosis
- Things that leads to Unstable mind
- Thoracoscopy
- three stages of chickenpox
- Thrombocytopenia and renal impairment
- thrombotic micro angiopathy
- Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
- Thunderclap headaches
- Thyroid gland
- Thyroid hormones
- Thyroid nodules
- Thyroid stimulating hormone
- Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
- Thyroiditis
- Thyroxine
- Tinea capitis
- tiredness
- To ease symptoms and prevent the spread of chickenpox
- TOF
- Toxemia of pregnancy
- Trachelectomy
- Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR)
- Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
- Transient arrhythmia
- transient Q waves
- Transmission of Chicken Pox
- Transposition of Great Vessels
- Treatment for Acid and Corrosive Poisoning
- Treatment for Acid Poisoning
- Treatment for acne
- Treatment for Acute Renal Failure
- Treatment for Adenoid disorders
- Treatment for Aortic Stenosis
- Treatment for Aortic Stenosis (AS)
- Treatment for Avascular Necrosis
- Treatment for Bladder Cancer
- Treatment for Carcinoma of Esophagus
- Treatment for Cervical carcinoma
- Treatment for Chicken Pox
- Treatment for corona virus
- Treatment for Corrosive Poisoning
- Treatment for Cyanotic Congenital Cardiac Defects
- Treatment for Depression
- Treatment for Deviated Nasal Septum
- Treatment for hypokalemia
- Treatment for Intestinal Tuberculosis
- Treatment for Mitral Incompetence
- Treatment for Mitral Regurgitation (MR)
- Treatment for Mitral Stenosis (MS)
- Treatment for Mood Swings
- Treatment for Pancreatitis
- Treatment for Patent Ductus Arteriosus
- Treatment for pimples
- Treatment for PRTA
- Treatment for Pulmonary Stenosis
- Treatment for Renal glycosuria
- Treatment for Shingles
- Treatment for Sinusitis
- Treatment for Sleeplessness
- Treatment for Submandibular lymphadenitis
- Treatment for suicidal ideation
- Treatment for Tetrology of Fallot
- Treatment for Truncus Arteriosus
- Treatment for Unstable Angina
- Treatment for Upper GI Bleeding
- Treatment for UTI
- Treatment for Ventricular Hypertrophy
- Treatment in Coarctation of Aorta
- Treatment in Cyanotic Congenital Cardiac Defects
- Treatment in Ebstein Anamoly
- Treatment in Ventricular Septal Defect
- Treatment in Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
- Treatment in VSD
- Treatment of acute Left Ventricular failure
- Treatment of acute LV failure
- Treatment Of Alopecia
- Treatment of Aortic Stenosis
- Treatment of Ascites
- Treatment of Atrial Septal Defect
- Treatment of Brain Tumors
- Treatment of Coarctation of Aorta
- Treatment of corona virus
- Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis
- Treatment of Demyelinating diseases
- Treatment of Fibromyalgia
- Treatment of Furuncle Nostril
- Treatment of Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia (GTN)
- Treatment of Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome
- Treatment of Ischemic Heart Disease
- Treatment of leukemia
- Treatment of Metabolic acidosis
- Treatment of Muscular dystrophy
- Treatment of Oral cancer
- Treatment of Pneumonia
- Treatment of Rhabdomyolysis
- Treatment of Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
- Treatment options for Pemphigus
- Treatment options in Cyanotic Congenital Cardiac Defects
- Treatment Perinatal Mood and Anxiety Disorders (PMADs)
- Treatments for body imbalance
- Tricuspid stenosis
- Triiodothyronine
- Triiodothyronine (T3)
- Tropical anhidrotic asthenia
- tropical impetigo
- Truncus Arteriosus
- TSH
- Tubular transport defects
- Tubulo-interstitial injury
- Two clinical subtypes of Pemphigus
- Two types of Polycystic kidney disease
- Types of Psoriasis
- Types of Angina Pectoris
- Types of Aortic Stenosis
- Types of Carcinoma of Esophagus
- Types of Cervical carcinoma
- Types of Coarctation of Aorta
- Types of Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia (GTN)
- Types of Heart Failure
- Types of Leukemia
- Types of Perinatal Mood and Anxiety Disorders
- Types of Persistant Truncus Arteriosus
- Types of pneumonia
- Types of Polycystic kidney disease
- Types of pulmonary stenosis
- Types of sinusitis
- Types of Sleeplessness (insomnia)
- Types of Transitional cell bladder cancer
- U wave inversion in ECG
- UGI scope
- Ultrasound examination
- unable to walk
- Uncommon causes of Ascites
- Underlying Causes
- Unexplained lymphadenopathy
- Unstable angina
- Unstable Angina in Detail
- Unstable mind
- Unsuitable bladder
- Unsuitable URETHRA
- unusual talktaveness
- Upper GI Bleeding
- Upper-Gastro-intestinal bleeding
- Urea clearance above 150 ml / min
- Ureteral anastomotic leak or occlusion
- Ureteral rupture
- Urethral obstruction
- urinary infection
- Urinary Tract Infection
- Urine quanitiative culture
- Urogenital Features of Cystic Fibrosis
- Use of Antihistamines in Anaphylaxis
- UTI
- Valvotomy
- Valvular Aortic Stenosis
- valvular heart disease
- Valvular Pulmonary Stenosis
- Variant Angina
- Variants in Transposition of Great Vessels
- varicella-zoster virus
- variety of brain tumors
- Various forms of renal replacement therapy in End Stage Renal Disease
- Vascular anastomotic leak of occlusion
- vasospastic symptoms
- ventricular aneursym
- Ventricular aneurysm
- Ventricular Hypertrophy
- Ventricular Hypertrophy in ECG
- Ventricular Septal Defect
- Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
- Vestibular rehabilitation therapy
- viral fever
- Viral Myositis
- Viral Myositis characterized by
- Viral pneumonia
- Viral sinusitis
- virus that causes chickenpox
- Visual disturbances
- Vitamin and mineral deficiencies linked to insomnia
- VSD
- VSD Closure
- VZV also causes shingles
- Walking on the toes
- walls of the heart's ventricles thicken
- ways cancer spreads in the body
- weakness and loss of muscle mass
- Weight loss
- Weil's disease
- Wheezes
- Whiteheads
- widespread pain
- Wound infection after kidney transplantation
- X ray findings in Ebstein Anamoly
- X- ray findings in Tetrology of Fallot
- X-Ray findings in Coarctation of Aorta
- X-Ray findings in Ventricular Septal Defect
- X-Ray findings in VSD
- Zits

www.medlight2u.com

Twitter @DrTamson

Instagram @drktamilselvan_mahasree