Sinusitis is an inflammation of the tissues in your sinuses (spaces in your forehead, cheeks and nose usually filled with air). It causes facial pain, a stuffy or runny nose, sneezing and sometimes a fever and other symptoms. It’s usually caused by the common cold, but other viruses, bacteria, fungi and allergies can also cause sinusitis. Sinusitis is also sometimes called rhinosinusitis.
It is a condition where the sinuses become inflamed, or swollen and red, due to a number of possible causes
A viral infection
A bacterial infection
A fungal infection
Blocked sinus openings
Too much mucus production
Structural issues in the nose, such as a Deviated Nasal Septum (DNS) or nasal polyps.
sinuses
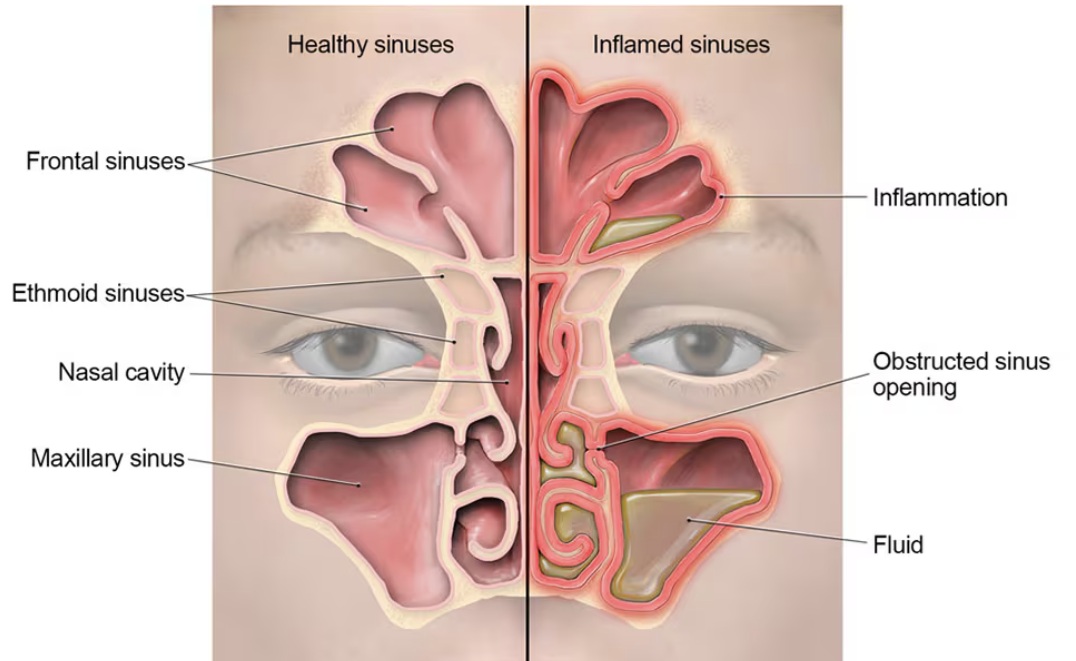
sinuses are four paired cavities (spaces) in your head. Narrow passages connect them. Sinuses make mucus that drains out of the passages in your nose. This drainage helps keep your nose clean and free of bacteria, allergens and other germs (pathogens).
Types of sinusitis
Types based on how long it’s been going on (Acute, Subacute, Chronic or Recurrent) and what’s causing it (Bacteria, Virus or Fungus).
Acute, subacute, chronic and recurrent sinusitis
Acute sinusitis symptoms (Sneezing, Nasal congestion, drainage, facial pain/pressure and decreased sense of smell) last less than four weeks. It’s usually caused by viruses like the common cold.
Subacute sinusitis symptoms last four to 12 weeks.
Chronic sinusitis symptoms last at least 12 weeks. Bacteria are usually the cause.
Recurrent acute sinusitis symptoms come back four or more times in one year and last less than two weeks each time.
Bacterial and viral
Viruses, like the ones that cause the common cold, cause most cases of sinusitis. Bacteria can cause sinusitis, or they can infect you after a case of viral sinusitis. If you have a runny nose, stuffy nose and facial pain that don’t go away after ten days, you might have bacterial sinusitis. Your symptoms may seem to improve but then return and are worse than the initial symptoms. Antibiotics and decongestants usually work well on bacterial sinusitis.
Fungal
Sinus infections caused by fungus are usually more serious than other forms of sinusitis. They’re more likely to happen if you have a weakened immune system.
causes of sinus infections
Viruses, bacteria, fungi and allergens can cause sinusitis.
Specific triggers
The common cold.
The flu (influenza).
Streptococcus pneumoniae bacteria.
Haemophilus influenza bacteria.
Moraxella catarrhalis bacteria.
Nasal and seasonal allergies.
Symptoms of sinusitis
Headache / Persistent Headache / Recurrent Headache
Sneezing recurrent episodes especially in the morning
Bad breath (halitosis) or a bad taste in your mouth or loss of smell
Cough, often worse at night
Fatigue and general feeling of being ill
Fever
Pressure-like pain, pain behind the eyes, toothache, or tenderness of the face
Nasal stuffiness and discharge/Stuffy nose.
Sore throat and postnasal drip.
Postnasal drip (mucus dripping down your throat).
Runny nose with thick yellow or green mucus.
Facial pressure (particularly around your nose, eyes and forehead). This might get worse when you move your head around or bend over.
Pressure or pain in your teeth.
Ear pressure or pain
Tiredness
Diagnosis
Nasal endoscopy
Nasal swabs a soft-tipped stick to get a fluid sample from your nose. They’ll test it for viruses or other germs that might be causing your symptoms.
Imaging In some cases, your provider might order a computed tomography (CT) scan to better understand what’s happening inside your sinuses.
Allergy testing If you have chronic sinusitis, your provider may test you for allergies that could be triggering it.
Biopsy Rarely, a provider may take a tissue sample from your nose for testing.
Treatment for Sinusitis
It can be treated with a number of approaches, including antibiotics, painkillers, decongestants, allergy medicines, steroids, and antifungal medicines.
Some things that might help prevent sinusitis
Not smoking, Avoiding other people’s smoke, Washing your hands often, and Staying away from things which are allergic to.
Nasal saline rinses.
Drinking plenty of fluids.
Oral or topical decongestants.
Prescribed intranasal sprays. (Don’t use nonprescription sprays or drops for longer than three to five days — they may actually increase congestion.)
Treat chronic sinusitis by focusing on the underlying condition.
Topical antihistamine sprays or oral pills.
Leukotriene antagonists, like montelukast.
Surgery to treat structural issues, polyps or fungal infections.
- Acid and Corrosive Poisoning
- Acne or Pimples
- Adrenal Glands
- Anaphylaxis
- Cardiopulmonary resuscitation
- Congenital Heart Disease
- Coronary Artery Diseases
- Diabetes
- ECG Analysis
- Emergency Medicine
- Fluids and Electrolytes
- Food and Nutrition
- Gastero-enterology
- Harmonal Disorders
- Heart Diseases
- Neurology
- Oncology
- ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Pituitary Gland
- Poisoning
- Psychiatry
- Respiratory Disorders
- Signs and Symptoms
- Skin Diseases
- Symptoms and Investigations
- Symptoms of Heart Diseases
- Thyroid Gland
- Urology
- Valvular Heart Diseases

Leave a Reply