Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia
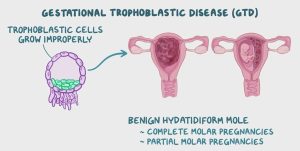
Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia (GTN) is a type of gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) that is typically malignant. GTN arises from abnormal growth of placental tissue in the uterus and can include conditions like invasive moles and choriocarcinomas. While rare, GTN is highly curable, especially in low-risk cases, and typically responds well to chemotherapy.
Types
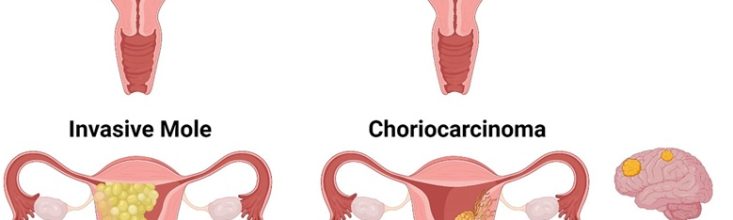
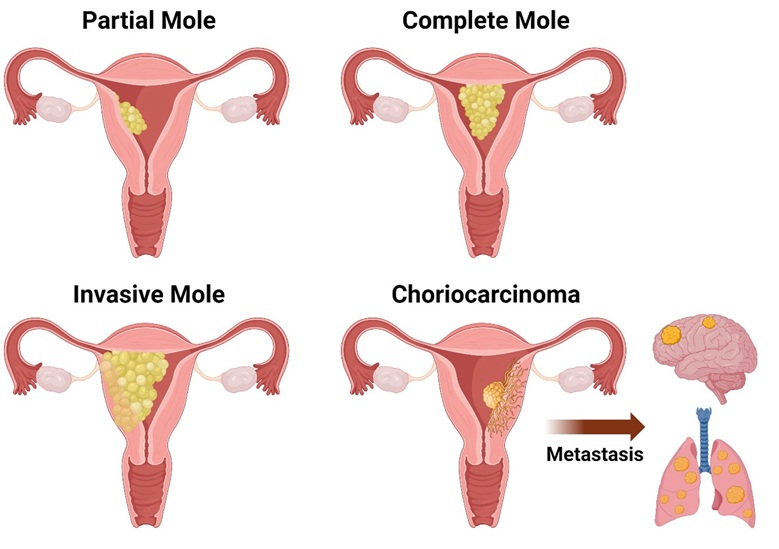
Choriocarcinoma
A cancerous tumor that can develop from molar pregnancies or after a miscarriage, abortion, or full-term pregnancy.
Invasive Mole (Chorioadenoma Destruens)
A cancerous growth that can develop from a molar pregnancy, rarely spreading outside the uterus.
Placental-Site Trophoblastic Tumor (PSTT)
A rare, slow-growing tumor that develops where the placenta attaches to the uterine wall.
Epithelioid Trophoblastic Tumor (ETT)
A rare tumor whose progression mimics PSTT.
Causes and Risk Factors of Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia (GTN)
Most GTN develop after a hydatidiform mole, which is a non-cancerous growth of placental tissue.
GTN can also occur after a miscarriage, abortion, ectopic pregnancy, or normal term pregnancy.
Risk factors include age (especially advanced maternal age), previous molar pregnancy, and certain medical conditions.
Signs and Symptoms
Abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Larger-than-expected uterus during pregnancy.
High levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) in the blood.
Pelvic pain or pressure.
Nausea and vomiting.
Other symptoms like cough, shortness of breath, headaches, or seizures are possible.
Diagnosis of GTN
Physical examination, including a pelvic exam.
Blood tests to check HCG levels.
Imaging studies like ultrasound or MRI.
Tissue biopsies to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment of Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia
Chemotherapy is the primary treatment for GTN.
Surgery, such as a dilation and curettage (D&C), may be used to remove tissue.
In some cases, a hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) may be necessary.
Prognosis
GTN is highly curable, especially in low-risk cases.
Even when the disease has spread, the prognosis is generally good, particularly if only the lungs are involved.
medlight2u.com
A light on Practice of Medicine (The information provided is for informational and educational purposes only and should not be considered professional advice)
Acne Acne vulgaris Acute Renal Failure Adrenal cortex Angina Angina Pectoris Aortic Regurgitation (AR) Aortic Stenosis (AS) Chest pain Chronic pyelonephritis Coarctation of Aorta Cough cyanosis Cystic acne Dehydration depression Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosis of Aortic Stenosis Dr.KTS DR K TAMILSELVAN Fatigue Heart Failure Hypertension Hypokalemia Hypothyroidism Ischemic Heart Disease LBBB Mitral Incompetence Mitral insufficiency Mitral valve prolapse Nocturia Patent Ductus Arteriosus PDA Polyuria Proteinuria pulmonary hypertension Pulmonary Stenosis ST Depression Symptoms of Acne Syncope Treatment for acne valvular heart disease Ventricular Septal Defect VSD Zits