End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
The term end stage renal disease (ESRD) means a renal disease which reaches the stage of irreversible renal failure also known as kidney failure, is a terminal illness that occurs when the kidneys can no longer filter waste from the blood.
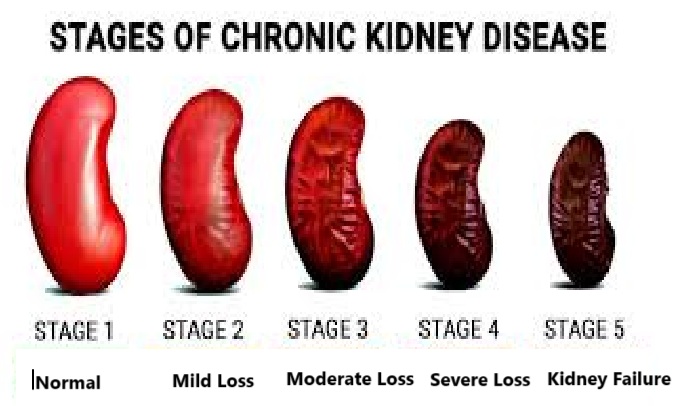
Common causes of End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
(i) Chronic glomerulonephritis
(ii) Nephrosclerosis
(iii) Chronic pyelonephritis
(iv) Diabetic glomerulosclerosis
(v) Polycystic kidney disease
(vi) Hypertensive nephrosclerosis
(vii) Diabetic nephropathy
(viii) Hypertension
(ix) Recurrent kidney infection
(x) Chronic obstruction
Symptoms of End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
Fatigue, drowsiness, dry skin, weight loss, nausea, bone pain, and changes to the skin and nails.
Treatment for End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
Dialysis or a kidney transplant is required to survive.
Life expectancy in End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
People on dialysis can live for 5–10 years on average, but many live for 20–30 years. Kidney transplants from living donors last 15–20 years, while those from deceased donors last 10–15 years.
Prevention of End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
Healthy lifestyle choices can help slow the progression of kidney disease,
including:
Maintaining a healthy weight
Being active most days
Limiting protein and eating a balanced diet
Controlling blood pressure
Taking medications as prescribed
Getting regular checkups
Various forms of renal replacement therapy in End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD)
Available are
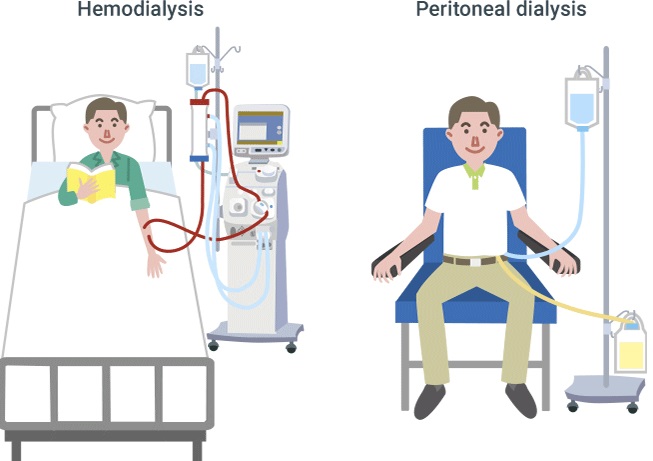
(i) Haemodialysis (HD)
(ii) Peritoneal dialysis (PD)
(iii) Intermittent peritoneal dialysis (IPD)
(iv) Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD)
(v) Kidney transplantation from a live-related donor or from a cadaveric donor.
medlight2u.com
Acne Acne vulgaris Acute Renal Failure Adrenal cortex Angina Angina Pectoris Aortic Regurgitation (AR) Aortic Stenosis (AS) Chest pain Chronic pyelonephritis Coarctation of Aorta Cough cyanosis Cystic acne Dehydration depression Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosis of Aortic Stenosis Dr.KTS DR K TAMILSELVAN Fatigue Heart Failure Hypertension Hypokalemia Hypothyroidism Ischemic Heart Disease LBBB Mitral Incompetence Mitral insufficiency Mitral valve prolapse Nocturia Patent Ductus Arteriosus PDA Polyuria Proteinuria pulmonary hypertension Pulmonary Stenosis ST Depression Symptoms of Acne Syncope Treatment for acne valvular heart disease Ventricular Septal Defect VSD Zits


Leave a Reply