Adenoids
Adenoids are a patch of tissue in the throat that help the body fight infection. Adenoids are part of your immune system. Located just behind your nasal passage, Adenoids help trap germs that enter your body through your nose and mouth. Adenoids begin to shrink around age 5 years Usually if there is no any hypertrophy and disappear by adulthood. A Part of lymphatic and immune system.
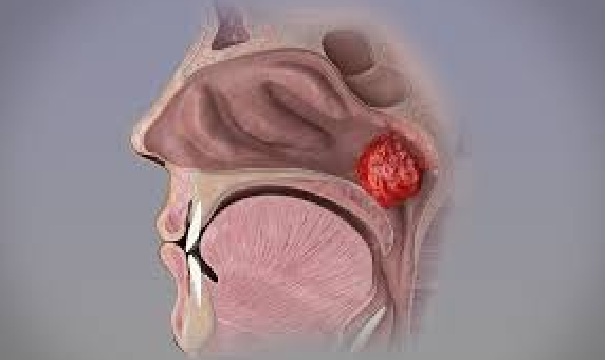
Adenoids have an important job for babies and young children. They help fight off germs until child’s body develops another way to combat infections. Adenoids also produce antibodies
Some interesting facts about adenoids
Adenoids grow to their maximum size between ages 3 and 5.
Adenoids start to shrink by age 7 or 8.
By adulthood, they’re completely gone.
Location of Adenoid
Adenoids are located in the upper airway, behind the nose and above the soft palate. Adenoids look like a pink patch of soft tissue. Some people describe the tissue mass as “cauliflower-like”. The average size of a normal (non-enlarged) adenoid is 6.2 millimeters. The average size of an enlarged adenoid is 11.6 millimeters. (Adenoids can become enlarged due to infection, allergies or other irritants.)
Functions of Adenoid
Adenoids are part of the lymphatic system, which helps the body fight infection and balance fluids. They trap germs that enter the body through the nose and mouth.
Development
Adenoids are especially important for babies and young children, but they usually start to shrink around age 5 and are almost gone by the teenage years. Adenoids are made of lymphoid tissue — the same type of tissue that your lymph nodes are made of. Lymphoid tissue consists of connective tissue and white blood cells, especially lymphocytes. Lymphocytes make antibodies and play a role in immune response.
Enlargement
Enlarged adenoids are most commonly due to
Frequent ear infections.
Upper respiratory infections.
Recurring (returning) nosebleeds.
Allergies.
Adenoids can swell up again with infections. Enlarged adenoids can cause problems, such as frequent ear and sinus infections, breathing problems, or sleep disturbances.
Enlarged adenoids can lead to
Sore throat.
Nasal congestion.
A feeling of fullness in their ears.
Mouth breathing.
Trouble sleeping.
Snoring.
Obstructive sleep apnea.
Diagnosis of Adenoid disorders
Imaging tests
To get a better view of child’s nasal passages, sinuses and adenoids, might take X-rays, CT scans or MRI.
Sleep study
If enlarged adenoids are causing obstructive sleep apnea or snoring, a sleep study may be needed.
Nasal endoscopy
During this test, inserts a flexible tube into child’s nose. The tube has a light and camera on the end so they can look at the adenoids directly. This way, they can tell if your child’s adenoids are red, inflamed or enlarged.
Bacteria culture test
To see if enlarged adenoids are the result of an infection may take a throat culture. This test determines which organisms or bacteria are present.
Treatment for Adenoid disorders
Adenoid can be treated conservatively in young Ages.
If adenoids are causing persistent problem, a doctor may recommend surgery to remove them, called an adenoidectomy.
Other treatments for adenoid issues include: Saline sprays or nasal rinses, Intranasal corticosteroids for allergies, and Antibiotics for bacterial infections.
medlight2u.com
A light on Practice of Medicine (The information provided is for informational and educational purposes only and should not be considered professional advice)
Acne Acne vulgaris Acute Renal Failure Adrenal cortex Angina Angina Pectoris Aortic Regurgitation (AR) Aortic Stenosis (AS) Chest pain Chronic pyelonephritis Coarctation of Aorta Cough cyanosis Cystic acne Dehydration depression Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosis of Aortic Stenosis Dr.KTS DR K TAMILSELVAN Fatigue Heart Failure Hypertension Hypokalemia Hypothyroidism Ischemic Heart Disease LBBB Mitral Incompetence Mitral insufficiency Mitral valve prolapse Nocturia Patent Ductus Arteriosus PDA Polyuria Proteinuria pulmonary hypertension Pulmonary Stenosis ST Depression Symptoms of Acne Syncope Treatment for acne valvular heart disease Ventricular Septal Defect VSD Zits

Leave a Reply