Left Atrial Enlargement
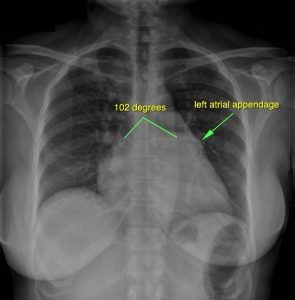
Lead II
P wave biphasic
Terminal negative component at least 0.04 second in duration and 1 mm deep (i.e., I mall square x 1 small square x 1 small square)
P axis to left (-300 or less)
Right Atrial Enlargement
Lead II
P peaked ( “P” pulmonale”) Greater than 2.5 mm height but duration normal.
Lead V1
Biphasic
Initial component 2.5 mm or greater or terminal component as in left atrial enlargement
May be entirely negative
P axis to right (+750 or more)
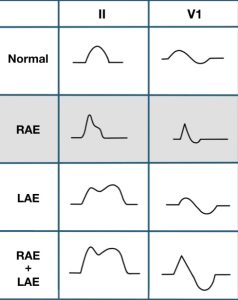
Right Atrial Enlargement occurs in
(1) Ebstein’s anomaly
(2) Cor pulmonale
(3) Tricuspid stenosis
(4) Pulmonary hypertension
Combined Atrial Enlargement
Lead II
P duration and amplitude both increased.
A dominant negative QRS complex in L1 suggests right axis deviation where as a dominant negative complex in aVF suggests left axis deviation. A tall RV1, greater than 5 mm or R/S in VI greater than 1 with ST depression and T inversion suggests right ventricular hypertrophy.
medlight2u.com
Acne Acne vulgaris Acute Renal Failure Adrenal cortex Angina Angina Pectoris Aortic Regurgitation (AR) Aortic Stenosis (AS) Chest pain Chronic pyelonephritis Coarctation of Aorta Cough cyanosis Cystic acne Dehydration depression Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosis of Aortic Stenosis Dr.KTS DR K TAMILSELVAN Fatigue Heart Failure Hypertension Hypokalemia Hypothyroidism Ischemic Heart Disease LBBB Mitral Incompetence Mitral insufficiency Mitral valve prolapse Nocturia Patent Ductus Arteriosus PDA Polyuria Proteinuria pulmonary hypertension Pulmonary Stenosis ST Depression Symptoms of Acne Syncope Treatment for acne valvular heart disease Ventricular Septal Defect VSD Zits

Leave a Reply