Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome (HUS)
Haemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS) is a syndrome of microangiopathic hemolytic anaemia, thrombocytopenia and renal impairment. It is due to glomerular endothelial cell injury by some unidentified circulating antigen.
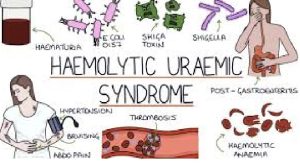
Causes of Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome
In children
3-10 days after gastroenteritis (due to E.coli), viral upper respiratory tract infection.
In adults
Pregnancy, oral contraceptive use, antineoplastic drugs.
Symptoms of Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome
HUS often begins with vomiting and diarrhea, which may be bloody. Within a week, the person may become weak and irritable. Persons with this condition may urinate less than normal. Urine output may almost stop.
Diagnosis of Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome
1.By history and physical examination,
2.Micro angiopathic haemolytic anemia with thrombocytopenia, reticulocytosis, raised serum bilirubin level,reduced haptoglobin level.
3.Raised levels of Fibrin degredation product (FDP) which indicates disseminated intra vascular coagulation (DIC).
4.Renal biopsy shows : Intimal hyperplasia of arterioles, intra capillary fibrin thrombin
Exams and Tests of Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome
- Blood clotting tests (PT and PTT)`
- Comprehensive metabolic panel may show increased levels of BUN and creatinine
- Complete Blood Count may show increased white blood cell count and decreased red blood cell count
- Platelet count is usually reduced
- Urinalysis may reveal blood and protein in the urine
- Urine protein test can show the amount of protein in the urine
- Kidney biopsy
- Stool culture may be positive for a certain type of E. coli bacteria or other bacteria
Treatment of Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome
A.Children
Early dialysis is required; but spontaneous recovery is common.
B.Adults
No definite therapy available. Different workers use aspirin, antiplatelet agents, heparin, fresh frozen plasma infusions, plasma exchange.
Possible Complications of Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome
- Blood clotting problems
- Hemolytic anemia
- Kidney failure
- Nervous system problems
- Too few platelets
- Uremia
Prognosis of Haemolytic Uremic Syndrome
This is a serious illness in both children and adults, and it can cause death. With proper treatment, more than half of patients will recover. The outcome is better in children than adults.
medlight2u.com
Acne Acne vulgaris Acute Renal Failure Adrenal cortex Angina Angina Pectoris Aortic Regurgitation (AR) Aortic Stenosis (AS) Chest pain Chronic pyelonephritis Coarctation of Aorta Cough cyanosis Cystic acne Dehydration depression Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosis of Aortic Stenosis Dr.KTS DR K TAMILSELVAN Fatigue Heart Failure Hypertension Hypokalemia Hypothyroidism Ischemic Heart Disease LBBB Mitral Incompetence Mitral insufficiency Mitral valve prolapse Nocturia Patent Ductus Arteriosus PDA Polyuria Proteinuria pulmonary hypertension Pulmonary Stenosis ST Depression Symptoms of Acne Syncope Treatment for acne valvular heart disease Ventricular Septal Defect VSD Zits

Leave a Reply