Headaches
Headaches are a very common condition that most people will experience many times during their lives. The main symptom of a headache is pain in your head or face. There are several types of headaches, and tension headaches are the most common. While most aren’t dangerous and certain types can be a sign of a serious underlying condition.

A headache is a pain in your head or face that’s often described as a pressure that’s throbbing, constant, sharp or dull. Headaches can differ greatly in regard to pain type, severity, location and frequency.
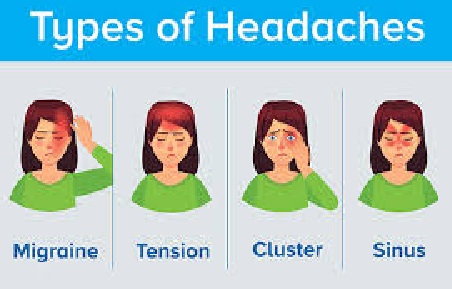
The types of headaches
There are more than 150 types and they fall into two main categories as Primary and Secondary
Migraine headache
Tension headache
Hormone headache
Exertion headache
Cluster headache
Allergy/sinus headache
Caffeine headache
Rebound headache
Hemicrania continua headache
Hypertension headache
Post-traumatic headache
Spinal headache
Thunderclap headache
Ice pick headache
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) headache
Primary headaches
Dysfunction or over-activity of pain-sensitive features in your head cause primary headaches. They’re not a symptom of or caused by an underlying medical condition. Some people may have genes that make them more likely to develop primary headaches.
Types of primary headaches include
Tension-type headaches (most common type of headache).
Migraine headache.
Cluster headache.
New daily persistent headaches (NDPH).
Some primary headaches can be triggered by lifestyle factors or situations
Alcohol particularly the red wine.
Certain foods, such as processed meats that contain nitrates (food-triggered headache).
Consuming nicotine (nicotine headache).
Changes in sleep or lack of sleep.
Poor posture.
Physical activity, such as exercise (exertion headaches).
Skipped meals (hunger headache).
Coughing, sneezing, blowing your nose, straining (such as when having a bowel movement), or laughing or crying vigorously (cough headaches).
Primary headache typically aren’t dangerous, but they can be very painful and disrupt your day-to-day life.
Secondary headaches
An underlying medical condition causes secondary headaches. They’re considered a symptom or sign of a condition.
Types of secondary headaches that aren’t necessarily dangerous and resolve once the underlying condition is treated
Dehydration headache.
Sinus headache.
Medication overuse headache.
Types of secondary headache that can be a sign of a serious or potentially life-threatening condition
Spinal headache
Spinal headache are intense headaches that occur when spinal fluid leaks out of the membrane covering your spinal cord, usually after a spinal tap. Most spinal headache can be treated at home, but prolonged, untreated spinal headaches can cause life-threatening complications, including subdural hematoma and seizures.
Thunderclap headache
A thunderclap headache is an extremely painful headache that comes on suddenly, like a clap of thunder. This type of headache reaches its most intense pain within one minute and lasts at least five minutes. While thunderclap headaches can sometimes be harmless, it’s important to seek immediate medical attention.
They can be signs of
Head injury.
Brain bleed.
Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome.
A sudden, severe rise in blood pressure.
The difference between a headache and a migraine
A migraine is a type of primary headache disorder.
A migraine is a common neurological condition that causes a variety of symptoms, most notably a throbbing headache on one side of your head. Migraines often get worse with physical activity, lights, sounds or smells. They usually last at least four hours or even days.
Anyone can have a headache, including children, adolescents and adults. About 96% of people experience a headache at least once in their life.
About 40% of people across the world have tension-type headaches and about 10% have migraine headache.
Symptoms and Causes of Headaches
The main cause of a headache
Headache pain results from signals interacting among your brain, blood vessels and surrounding nerves. During a headache, multiple mechanisms activate specific nerves that affect muscles and blood vessels. These nerves send pain signals to your brain, causing a headache.
Are headaches hereditary
Headache tend to run in families, especially migraines. Children who have migraines usually have at least one biological parent who also experiences them. In fact, kids whose parents have migraines are up to four times more likely to develop them.
Headache can also be triggered by environmental factors shared in a family’s household
Eating certain foods or ingredients, like caffeine, alcohol, fermented foods, chocolate and cheese.
Exposure to allergens.
Secondhand smoke.
Strong odors from household chemicals or perfumes.
Headache symptoms require immediate medical care
A sudden, new and severe headache.
ith a fever, shortness of breath, stiff neck or rash.
Headaches that occur after a head injury or accident.
Getting a new type of headache after age 55.
Associated with neurological symptoms
Weakness.
Dizziness.
Sudden loss of balance or falling.
Numbness or tingling.
Paralysis.
Speech difficulties.
Mental confusion.
Seizures.
Personality changes/inappropriate behavior.
Vision changes (blurry vision, double vision or blind spots).
Diagnosis and Tests for headache
During the evaluation, history, including
What the headache feel like…?
How often the headache happen…?
What foods, drinks or events trigger your headache…?
How long last each time…..?
How much pain the headaches cause you…..?
What your stress level is…..?
How much caffeine you drink each day…..?
What your sleep habits are like….?
Headache can be more accurately diagnosed by knowing
When the headache started…?
Whether there’s a single type of headache or multiple types of headache…?
If physical activity aggravates the headache pain…?
Who else in your family has headache…?
What symptoms, if any, occur between headache…?
Physical and Neurological examinations of Headache
Fever.
Infection.
High blood pressure.
Muscle weakness, numbness or tingling.
Excessive fatigue.
Loss of consciousness.
Balance problems and frequent falls.
Vision problems (blurry vision, double vision, blind spots).
Mental confusion or personality changes.
Seizures.
Dizziness.
Nausea and vomiting.
Neurological tests focus on ruling out diseases that might also cause headache. A disorder of your central nervous system might be suspected in the development of serious headache.
After evaluating the results of your headache history, physical examination and neurological examination, your physician should be able to determine what type of headache you have, whether or not a serious problem is present and whether additional tests are needed.
If they’re unsure of the cause, they may refer you to a headache specialist.
Diagnosis of headaches
Although scans and other imagining tests can be important when ruling out other diseases, they don’t help in diagnosing migraines, cluster or tension-type headache.
A CT scan or MRI can help determine if your headaches are connected to an issue with your central nervous system. Both of these tests produce cross-sectional images of your brain that can show any abnormal areas or problems.
Treatment for Headaches
Treatment depends on the type.
One of the most crucial aspects of treating primary type is figuring out your triggers. Learning what those are — typically by keeping a headache log — can reduce the number of headaches you have.
Once you know your triggers, your healthcare provider can tailor treatment to you. For example, you may get headache when you’re tense or worried. Counseling and stress management techniques can help you handle this trigger better. By lowering your stress level, you can avoid stress-induced headache.
Not every headache requires medication. A range of treatments is available.
Depending on your headache type, frequency and cause, treatment options include
Stress management.
Biofeedback.
Medications.
Treating the underlying medical condition
Stress management for headache
Stress management teaches you ways to cope with stressful situations. Relaxation techniques help manage stress. You use deep breathing, muscle relaxation, mental images and music to ease your tension.
Biofeedback for headache
Biofeedback teaches you to recognize when tension is building in your body. You learn how your body responds to stressful situations and ways to settle it down. During biofeedback, sensors are connected to your body. They monitor your involuntary physical responses, which include increases in:
Breathing rate.
Pulse.
Heart rate.
Temperature.
Muscle tension.
Brain activity.
Medications for headaches
Occasional tension headaches usually respond well to over-the-counter pain relievers. But be aware that using these medications too often can lead to long-term daily episodes (medication overuse headaches).
For frequent or severe headaches, your provider may recommend prescription headache medications. Triptans and other types of drugs can stop a migraine attack. You take them at the first signs of an oncoming headache.
Drugs for high blood pressure, seizures and depression can sometimes prevent migraines.
Treating the underlying medical condition causing secondary headache
Treatment for secondary type involves treating the underlying medical condition causing it.
For example, surgery is often needed to correct the underlying cause of secondary cough headache.
Treat the occasional, mild headache at home with over-the-counter pain relievers.
Other self-care treatments include
Applying heat or cold packs to your head.
Doing stretching exercises.
Massaging your head, neck or back.
Resting in a dark and quiet room.
Taking a walk.
Prevention of headaches
The key to preventing is figuring out what triggers them. Triggers are very specific to each person
what gives you a headache may not be a problem for others.
Once you determine your triggers, you can avoid or minimize them.
For example, you may find that strong scents set you off. Avoiding perfumes and scented products can make a big difference in how many headaches you have. The same goes for other common triggers like troublesome foods, lack of sleep and poor posture.
Many people, however, aren’t able to avoid triggers or are unable to identify triggers. In that case, a more personalized multidisciplinary approach with a headache specialist is often necessary.
Prognosis of Headaches
Treating health problems that cause, such as high blood pressure, can eliminate head pain. Recently, there have been several new advancements in our understanding of what causes it.
Although researchers are closer than ever before to a cure, at this time, there isn’t a cure for primary type.
Treatment focuses on relieving symptoms and preventing future episodes.
Living With if you or your child has any of the following symptoms or situations:
Experiencing one or more episodes per week.
Experiencing it keep getting worse and won’t go away.
Needing to take a pain reliever every day or almost every day.
Needing more than two to three doses of over-the-counter medications per week to relieve headache symptoms.
Experiencing that are triggered by exertion, coughing, bending or strenuous activity.
Having a history but experiencing a recent change in your headache symptoms.

Leave a Reply