Leukemia-Commonly as Blood Cancer
Leukemia is a type of cancer that affects the blood and bone marrow, causing the body to produce too many abnormal white blood cells. These abnormal cells, called blasts or leukemia cells, are unable to fight infection and crowd out healthy blood cells.
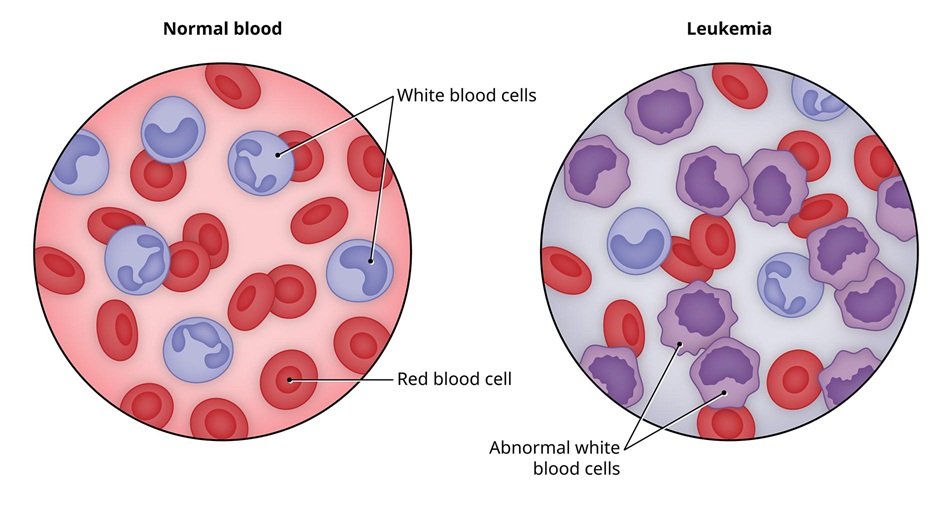 Leukemia Blood Cancer[/caption] <p>Many types of leukemia exist. Some forms of leukemia are more common in children. Leukemia usually involves the white blood cells. Your white blood cells are potent infection fighters — they normally grow and divide in an orderly way, as your body needs themin people with leukemia, the bone marrow produces an excessive amount of abnormal white blood cells, which don’t function properly.
Leukemia Blood Cancer[/caption] <p>Many types of leukemia exist. Some forms of leukemia are more common in children. Leukemia usually involves the white blood cells. Your white blood cells are potent infection fighters — they normally grow and divide in an orderly way, as your body needs themin people with leukemia, the bone marrow produces an excessive amount of abnormal white blood cells, which don’t function properly.
Causes of Leukemia
<p>Research don’t understand the exact causes. It seems to develop from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Mature, normal blood cells.
Red blood cells
Cells that carry oxygen and other vital materials to all tissues and organs in your body.
White blood cells
Cells that fight infection.
Platelets
Cells that help your blood clot.
These blood cells start as hematopoietic (hemo = blood, poiesis = make) stem cells.
Myeloid cells develop into red blood cells, platelets and certain types of white blood cells (basophils, eosinophils and neutrophils).
Lymphoid cells develop into certain white blood cells (lymphocytes and natural killer cells).
One of the developing blood cells begins to multiply out of control. These abnormal cells called leukemia cells begin to take over the space inside of your bone marrow. They crowd out the cells trying to develop into healthy red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
Occur some blood cells acquire changes (mutations) in their genetic material or DNA. A cell’s DNA contains the instructions that tell a cell what to do. Normally, the DNA tells the cell to grow at a set rate and to die at a set time. the mutations tell the blood cells to continue growing and dividing.
Happens, blood cell production becomes out of control. Over time, these abnormal cells can crowd out healthy blood cells in the bone marrow, leading to fewer healthy white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets, causing the signs and symptoms.
Symptoms of Leukemia
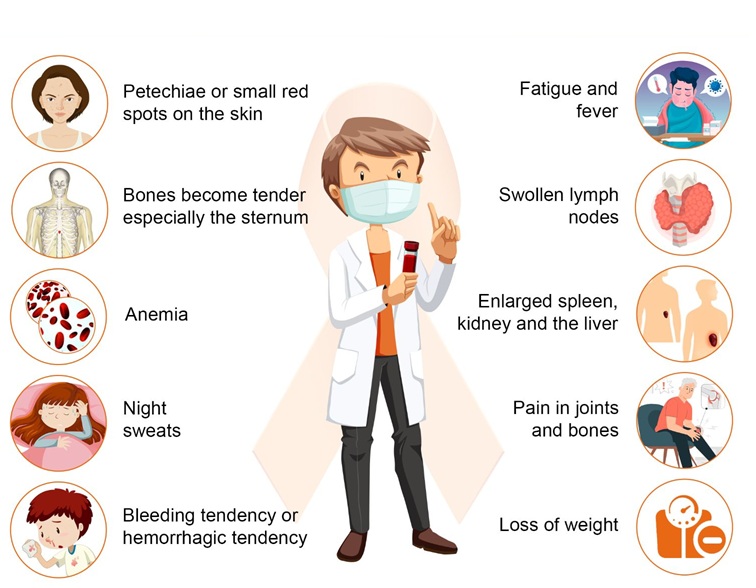
Bleeding and bruising
Bone pain
Fatigue
Fever
Increased risk of infections
Weight loss without trying
Swollen lymph nodes
Enlarged liver or spleen
Easy bleeding or bruising
Recurrent nosebleeds
Types of Leukemia
<p>The first type of classification is by how fast the leukemia progresses. The actual classification based on its speed of progression and the type of cells involved.
Acute leukemia
This type affects immature cells and grows quickly, requiring immediate treatment. In acute leukemia, the abnormal blood cells are immature blood cells (blasts). Cannot carry out their normal functions, and they multiply rapidly, the disease worsens quickly. Acute leukemia requires aggressive, timely treatment.
Chronic leukemia
This type affects mature or partially mature cells and grows more slowly. There are many types of chronic leukemias. Some produce too many cells and some less. Chronic leukemia involves more mature blood cells. These blood cells replicate or accumulate more slowly and can function normally for a period of time.
Classification by type of white blood cell affected
Lymphocytic leukemia
This type affects the lymphoid cells (lymphocytes), which form lymphoid or lymphatic tissue. Lymphatic tissue makes up your immune system. A type of white blood cell that plays a role in the immune system.
Myelogenous leukemia
This type affects the cells that mature into red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. This type of leukemia affects the myeloid cells. Myeloid cells give rise to red blood cells, white blood cells and platelet-producing cells.
Diagnostically there are four main types
Acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL)
The
most common type in children, teens and young adults up to age 39. ALL can affect adults of any age.
Acute myelogenous leukemia (AML)
The most common type in adults. It’s more common in older adults (those over 65). AML occurs in children.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)
The
most common chronic leukemia in adults (most common in people over 65). Symptoms may not appear for several years with CLL.
Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)
Mo
re common in older adults (most common in people over 65) can affect adults of any age. It rarely occurs in children. Symptoms may not appear for several years with CML.
Diagnosis of Leukemia
A needle suctioning out liquid bone marrow from hipbone
Bone marrow exam
Enlarge image
Physical examination
Physical signs, pale skin from anemia, swelling of your lymph nodes, and enlargement of your liver and spleen.
Blood tests
Looking at a sample of your blood, abnormal levels of red or white blood cells or platelets which may suggest leukemia.
Bone marrow test
Sometimes the leukemia cells stay in the bone marrow. Physician may recommend a procedure to remove a sample of bone marrow from your hipbone. The bone marrow removed by a needle.
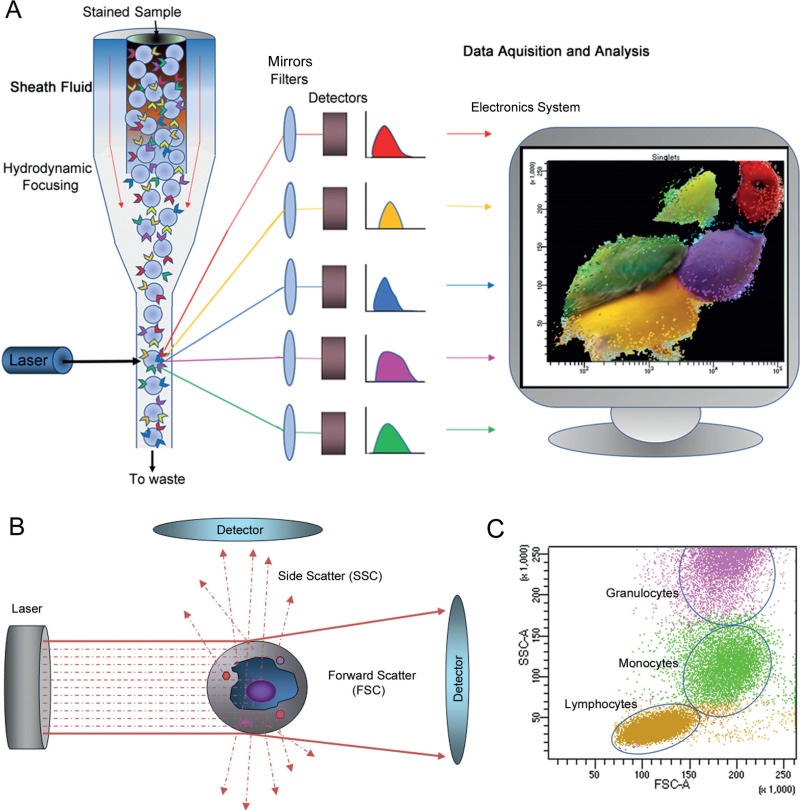
Flow cytometry
Flow cytometry is a test that uses a laser to analyze cells in a sample to diagnose leukemia. It’s a powerful tool that can quickly identify abnormal cell populations and determine the type.
A lab technician places a sample of blood, bone marrow, or tissue in a liquid suspension.
The technician treats the cells with fluorescent antibodies.
The sample injected into a flow cytometer.
1.Passes the cells in a single line in front of a laser beam.
2. Counts and categorizes the cells based on how the laser light scatters off them.
3.Sends the data to a computer, which generates a report.
Leukemia and Flow Cytometry
<p>Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL),
Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML),
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL), and
<p>Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML).
Lymphoma</p>
Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma and multiple myeloma.
Tumor lineage
Flow cytometry can help identify the tumor lineage as T cell, B cell, or myeloid.
DNA ploidy
Flow cytometry can help determine DNA ploidy, which can help with diagnosis and prognosis.
A flow cytometry leukemia panel is a test that uses a flow cytometer to analyze white blood cells for the presence of leukemia. The test to monitor and classify it as a subtype.
Procedure of Flow cytometry
A sample of blood, bone marrow, tissue, or fluid stained with monoclonal antibodies
The antibodies bind to antigens on the cell surface, in the cytoplasm, or in the nucleus
The flow cytometer measures the physical characteristics and markers of the cells
A hematopathologist analyzes the results to identify and diagnose leukemia
In Flow cytometry can quickly diagnose leukemia
It can help determine a prognosis and treatment options
It can help monitor the progress after treatment
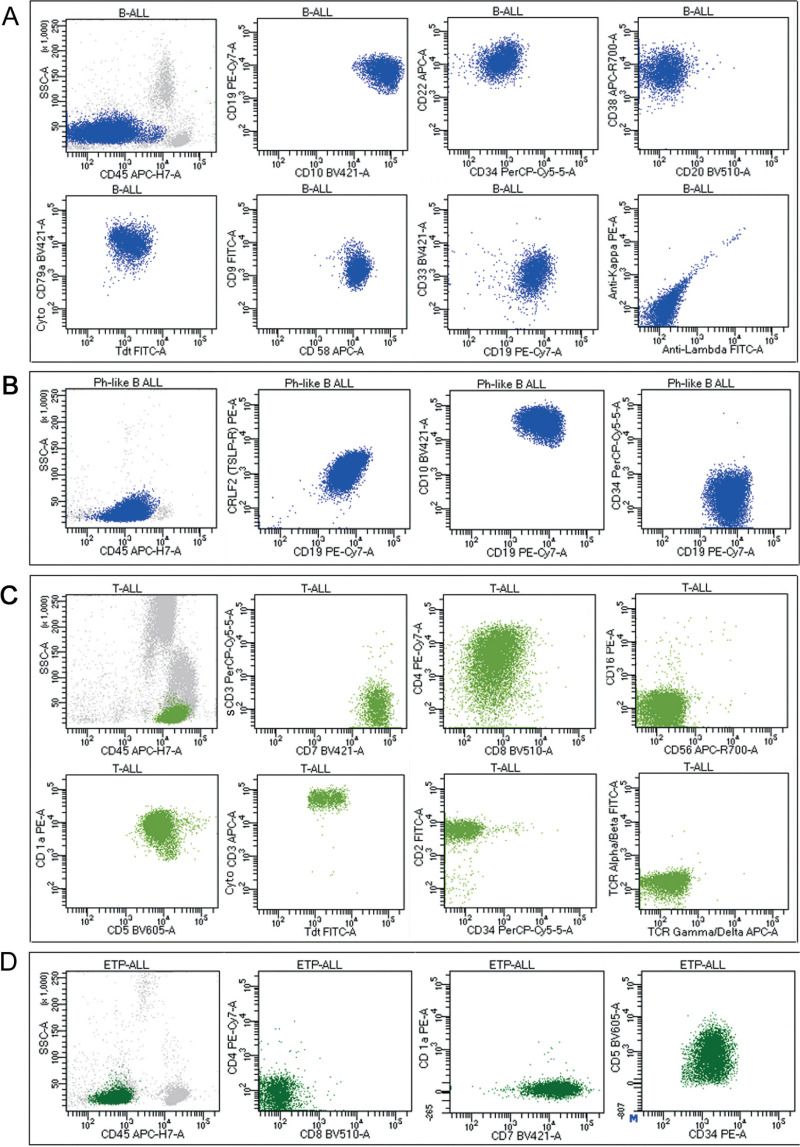
Leukemia/Lymphoma Phenotyping Evaluation by Flow Cytometry
Leukemia and lymphoma analysis by flow cytometry aids identifying the tumor lineage. Most cases identified T cell, B cell, or myeloid. Lineage identification can provide a confirmatory diagnosis or differential diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment options.
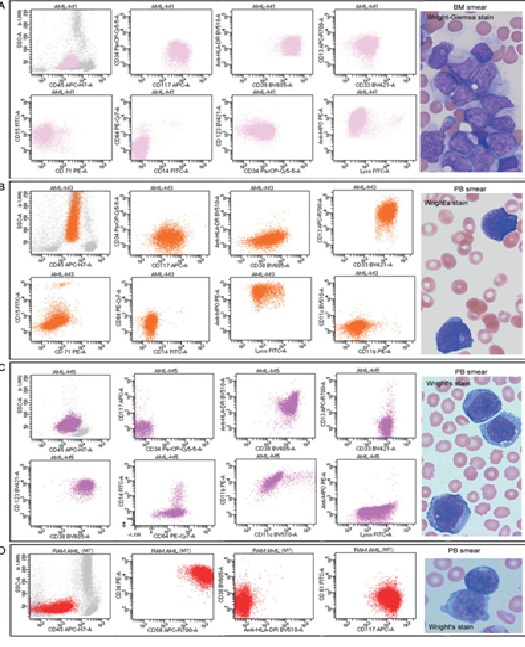 Flow cytometry AML
Flow cytometry AML
Diagnosis/Treatment Issues regarding Method Flow Cytometry
Phenotyping by flow cytometry can aid in the evaluation of hematopoietic neoplasms.
Specimens include bone marrow, whole blood, tissue, or fluid.
Phenotyping may aid in monitoring response to therapy in individuals with an established diagnosis of hematopoietic neoplasms.
Test Interpretation
Markers analyzed as needed, based on clinical evidence, to fully characterize any abnormalities identified by the screening panel.
Additional markers interpretation of the screening panel results.
Antigens included:
T cell: CD1a, CD2, CD3, CD4, CD5, CD7, CD8, TCR γ-δ, cytoplasmic CD3
B cell: CD10, CD19, CD20, CD22, CD23, CD103, CD200, kappa, lambda, cytoplasmic kappa, cytoplasmic lambda
Myeloid/monocyte: CD11b, CD13, CD14 (Mo2), CD14 (MY4), CD15, CD33, CD64, CD117, myeloperoxidase
Miscellaneous: CD11c, CD16, CD25, CD30, CD34, CD38, CD41, CD42b, CD45, CD56, CD57, CD61, HLA-DR, glycophorin, TdT, bcl-2, ALK-1, CD123, CD138, CD200, CD26, CD45, CRLF-2
Clinical Sensitivity
Limit of detection is 0.01–1.0% depending on phenotype and disease.
Results
Antigens reported as positive or negative.
Interpretive comments characterize intensity patterns included.
Dim, bright, variable, or partial reported.
Light-chain expression reported as polytypic/polyclonal or restricted/monotypic/monoclonal.
May include kappa/lambda ratio.
Limitations
Some hematopoietic neoplasms do not show phenotypic abnormalities and may not detected by flow cytometry.
Poor cell viability may adversely affect antigens and impede the ability to properly identify neoplastic cells.
Flow results cannot used alone to diagnose malignancy.
Results should interpreted in conjunction with morphology, clinical information, and other necessary ancillary tests for a definitive diagnosis.
Treatment of leukemia
Treatment depends on the type.
Research has led to improved outcomes for children diagnosed with it. Treatment depends on many factors.
Common treatments used to fight the disease.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the major form of treatment. This drug treatment uses chemicals to kill leukemia cells.
Depending on the type of leukemia you have, you may receive a single drug or a combination of drugs. These drugs may come in a pill form, or injected directly into a vein.
Targeted therapy
Targeted drug treatments focus on specific abnormalities present within cancer cells. By blocking these abnormalities, targeted drug treatments can cause cancer cells to die.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses X-rays or other high-energy beams to damage leukemia cells and stop their growth.
You may receive radiation in one specific area of your body where there is a collection of leukemia cells, or you may receive radiation over your whole body. Radiation therapy used to prepare for a bone marrow transplant.
Bone marrow transplant
Bone marrow transplant, also called a stem cell transplant, helps re-establish healthy stem cells by replacing unhealthy bone marrow with leukemia-free stem cells that will regenerate healthy bone marrow.
Prior to a bone marrow transplant, very high doses of chemotherapy or radiation therapy to destroy the leukemia-producing bone marrow.</p>
Then receive an infusion of blood-forming stem cells that rebuild the bone marrow.
You may receive stem cells from a donor or you may be able to use your own stem cells.
Immunotherapy
Uses immune system to fight cancer. Body’s disease-fighting immune system may not attack your cancer because the cancer cells produce proteins that help them hide from the immune system cells. Immunotherapy works by interfering with that process.
Engineering immune cells to fight leukemia. A specialized treatment called chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy takes your body’s germ-fighting T cells, engineers them to fight cancer and infuses them back into your body. CAR-T cell therapy might be an option for certain types of leukemia.
Clinical trials. Clinical trials are experiments to test new cancer treatments and new ways of using existing treatments. While clinical trials give you or your child a chance to try the latest cancer treatment, treatment benefits and risks may be uncertain. Discuss the benefits and risks of clinical trials with your doctor.
The phases of Leukemia Treatment</strong>
<p>Depending on treatment plan, may receive ongoing leukemia treatments long-term or treatment in phases. Phased treatment involves three parts. Each phase has a specific goal.
Induction therapy. The goal is to kill as many leukemia cells as possible in your blood and bone marrow to achieve remission. In remission, blood cell counts return to normal levels, no leukemia cells found in blood, and all signs and symptoms of disease disappear. Induction therapy usually lasts four to six weeks.
Consolidation (also called intensification). The goal is to kill any remaining undetected leukemia cells, so the cancer doesn’t return. You’ll usually receive consolidation therapy in cycles, over four to six months.
Maintenance therapy. The goal is to kill any leukemia cells that may have survived the first two treatment phases and prevent the cancer from returning (relapse). Treatment lasts about two years.
Prognosis in Leukemia
<p>It’s difficult to predict the prognosis because everyone’s experience is different. Outcomes depend on a variety of factors,
Genetic abnormalities or mutations
The mutations inside leukemia cells are the most important predictor of outcome.
Type of leukemia
Certain types associated with more favorable outcomes.
Blood cell counts at the time of diagnosis
The number of leukemia cells at your diagnosis can play a role in your outcome.
Age
Generally, the younger are at the diagnosis, better your outcome.
Health
Generally, the healthier you are at your diagnosis, the better your outcome.
Response to treatment
The length of time it takes for cancer to go into remission often indicates how successful treatment may be.
Presence of leukemia cells in your central nervous system
Cells in your spinal fluid are often more difficult to treat.
Ultimately
your Doctor is the most reliable resource for understanding how your cancer affects your unique prognosis. Ask them about treatment outcomes.
The survival rate of leukemia
Although the number of new cases in the U.S. has remained relatively steady or slightly increased since the 1970s, the survival rate has also improved. Still, long-term outcomes vary for each person.
survival compares patients diagnosed with cancer vs. people of same age, race and sex who are cancer free.
There isn’t a cure for leukemia, <strong>but this doesn’t mean some people don’t achieve long-term remission.
Risk factors in Leukemia
Factors that may increase your risk of developing some types.
Previous cancer treatment.
People who’ve had certain types of chemotherapy and radiation therapy for other cancers have an increased risk of developing certain types.
Genetic disorders.
Genetic abnormalities seem to play a role in the development. Certain genetic disorders, Down syndrome, associated with an increased risk.
Exposure to certain chemicals.
Exposure to certain chemicals, such as benzene which found in gasoline and used by the chemical industry linked to an increased risk of some kinds.
Smoking. Smoking cigarettes increases the risk of acute myelogenous leukemia.
Family history-If members of family diagnosed, risk of the disease possibility increased.
HELP LINE https://www.indiancancersociety.org/contact-us/
medlight2u.com
A light on Practice of Medicine (The information provided is for informational and educational purposes only and should not be considered professional advice)
Acne (2) Acne vulgaris (2) Acute Renal Failure (2) Adrenal cortex (2) Angina (2) Angina Pectoris (2) Aortic Regurgitation (AR) (2) Aortic Stenosis (AS) (2) Chest pain (3) Chronic pyelonephritis (3) Coarctation of Aorta (2) Cough (2) cyanosis (3) Cystic acne (2) Dehydration (2) depression (4) Diabetes Mellitus (3) Diagnosis of Aortic Stenosis (2) Dr.KTS (35) DR K TAMILSELVAN (36) Fatigue (2) Heart Failure (2) Hypertension (2) Hypokalemia (2) Hypothyroidism (2) Ischemic Heart Disease (2) LBBB (2) Mitral Incompetence (2) Mitral insufficiency (2) Mitral valve prolapse (2) Nocturia (2) Patent Ductus Arteriosus (2) PDA (2) Polyuria (2) Proteinuria (3) pulmonary hypertension (2) Pulmonary Stenosis (2) ST Depression (2) Symptoms of Acne (2) Syncope (3) Treatment for acne (2) valvular heart disease (2) Ventricular Septal Defect (2) VSD (2) Zits (2)


Leave a Reply