Submandibular lymphadenitis
Submandibular lymphadenitis is swelling of the lymph nodes under the lower jaw. It can be caused by a number of infections, including respiratory infections, sexually transmitted diseases, and bacterial infections.
Lymphadenitis is the inflammation or enlargement of a lymph node.
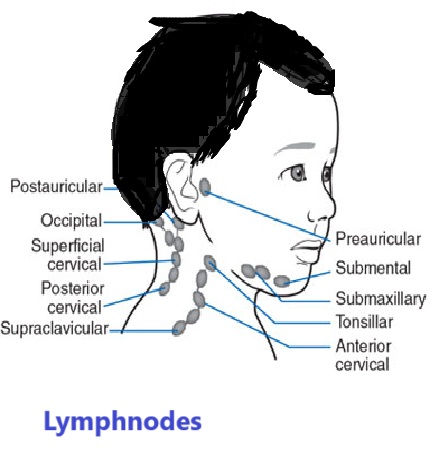
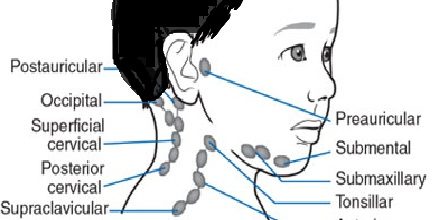
Lymph nodes
Lymph nodes are small, oval-shaped nodules that filter out microorganisms and abnormal cells from lymph fluid.
Symptoms of Submandibular lymphadenitis
Swollen, tender, and hot lymph nodes.
Fever, fatigue, and muscle aches.
Redness or red streaking of the skin over the nodes.
Fluid draining from the nodes to the skin.
Causes of Submandibular lymphadenitis
Noncarcinogenic and noninfectious illnesses such as drug-induced lymphadenopathy, collagen vascular disorders, and sarcoidosis may also cause generalized or localized adenopathy.
Epstein-Barr virus.
Cytomegalovirus.
Cat-scratch disease.
Tuberculosis.
Sexually transmitted diseases.
Bacterial infections.
Bilateral upper respiratory disorders, such as sinusitis.
Generalized respiratory infections, such as equine influenza.
Diagnosis of Submandibular lymphadenitis
In general, the presence or absence of other signs and symptoms, changes in the nodes over time, and the characteristics of the nodes themselves determine how assertive any diagnostic plan should be.
For example, a patient with a movable, stable, soft node in the neck who is otherwise healthy can be observed for months. On the other hand, hard axillary (armpit) or supraclavicular (above the collarbone) nodes raise the suspicion of cancer and require aggressive biopsy (a procedure to sample lymph node tissue).
If adenopathy is chronic in one area, a thorough physical examination will determine if other less obvious nodes are involved, and palpating the liver and spleen may help determine the extent of involvement, particularly significant in lymphoma. Persistent, generalized (throughout the body) lymphadenopathy with no other signs is unusual and requires testing.
Treatment for Submandibular lymphadenitis
Antibiotics, antivirals, or antifungals.
Medicine to control pain and fever.
Medicine to reduce swelling.
Surgery to drain a lymph node that has filled with pus.
Risk Factors
Unexplained lymphadenopathy.
Difficulty breathing or swallowing.
More details
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/conditions-and-diseases/lymphadenitis
medlight2u.com
A light on Practice of Medicine (The information provided is for informational and educational purposes only and should not be considered professional advice)
Acne Acne vulgaris Acute Renal Failure Adrenal cortex Angina Angina Pectoris Aortic Regurgitation (AR) Aortic Stenosis (AS) Chest pain Chronic pyelonephritis Coarctation of Aorta Cough cyanosis Cystic acne Dehydration depression Diabetes Mellitus Diagnosis of Aortic Stenosis Dr.KTS DR K TAMILSELVAN Fatigue Heart Failure Hypertension Hypokalemia Hypothyroidism Ischemic Heart Disease LBBB Mitral Incompetence Mitral insufficiency Mitral valve prolapse Nocturia Patent Ductus Arteriosus PDA Polyuria Proteinuria pulmonary hypertension Pulmonary Stenosis ST Depression Symptoms of Acne Syncope Treatment for acne valvular heart disease Ventricular Septal Defect VSD Zits

Leave a Reply